Characterisation of Primary Human Hippocampal Astrocyte Cell Culture Following Exposure to Hypoxia
- PMID: 36875187
- PMCID: PMC9984107
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2023.30.1.8
Characterisation of Primary Human Hippocampal Astrocyte Cell Culture Following Exposure to Hypoxia
Abstract
Background: The present study aimed to understand the characterisation of human hippocampal astrocyte following hypoxia exposure. Based on the preliminary screening, 15 min was chosen as the time point and the cells were exposed to different oxygen percentages.
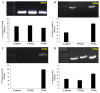
Methods: The Trypan blue viability assay used to examine cell death. Immunofluorescence assay, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was used to portray the morphology of astrocytes. The hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) staining was performed to confirm hypoxia induced cell death and there was a dramatic expression of HIF-1α displayed in exposed astrocyte cells compared to the control. In molecular level, genes were chosen, such as glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), GFAP, HIF-1α and B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and ran the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
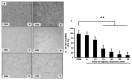
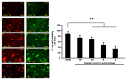
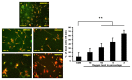
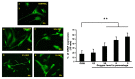
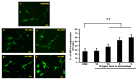
Results: Microscope revealed a filamentous and clear nucleus appearance in a control whereas the rupture nuclei with no rigid structure of the cell were found in the 3% oxygen. The control and hypoxia cells were also stained with the annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (annexin V-FITC). Fluorescence microscope reveals astrocyte cells after hypoxia showed higher expression of nuclei but not in control. Merging PI and FITC showed the differences of nuclei expression between the control and hypoxia. In the molecular analysis, there were significant changes of GFAP, HIF-1α and Bcl-2 in hypoxia exposed cells when compared to the control group.
Conclusion: Cells that were exposed to hypoxia (3% oxygen for 15 min) clearly showed damage. General view of human hippocampal astrocyte genomic response to hypoxia was obtained.
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma 2; HIF-1α; annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate staining; cell viability; glial fibrillary acidic protein marker; glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; human hippocampal astrocytes; hypoxia; morphological changes; oxygen percentage.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tanshinone IIA dampens the cell proliferation induced by ischemic insult in rat astrocytes via blocking the activation of HIF-1α/SDF-1 signaling.Life Sci. 2014 Sep 1;112(1-2):59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.07.020. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25064828
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 protects hypoxic astrocytes against glutamate toxicity.ASN Neuro. 2012 May 30;4(4):231-41. doi: 10.1042/AN20120006. ASN Neuro. 2012. PMID: 22540931 Free PMC article.
-
The HIF-1 inhibitor YC-1 decreases reactive astrocyte formation in a rodent ischemia model.Am J Transl Res. 2015 Apr 15;7(4):751-60. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26064442 Free PMC article.
-
Thiamine deficiency activates hypoxia inducible factor-1α to facilitate pro-apoptotic responses in mouse primary astrocytes.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0186707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186707. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29045486 Free PMC article.
-
A(1) and A(3) adenosine receptors inhibit LPS-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1 accumulation in murine astrocytes.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Oct;76:157-70. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23969284
References
-
- Barhwal K, Hota SK, Jain V, Prasad D, Singh SB, Ilavazhagan G. Acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) prevents hypobaric hypoxia-induced spatial memory impairment through extracellular related kinase-mediated nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 phosphorylation. Neuroscience. 2009;161(2):501–514. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.02.086. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
