Efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine injection for diabetic kidney disease: A network meta analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 36874023
- PMCID: PMC9981802
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1028257
Efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine injection for diabetic kidney disease: A network meta analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is an important public health problem worldwide that increases the mortality of patients and incurs high medical costs. Traditional Chinese Medicine injections (TCMIs) are widely used in clinical practice. However, their efficacy is unknown owing to a lack of definitive evidence. This study conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine injections in the treatment of DKD to provide a reference for clinical treatment. Methods: Total 7 databases had been searched, which included PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese scientific journal database (VIP), WanFang, and SinoMed. Only randomised controlled trials (RCT) had been included for analysis. The retrieval time limit was from the establishment of the database until 20 July 2022. Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool was used to evaluate the quality of the studies. Network meta-analyses, and Trial Sequential Analyses (TSA) were used to analysis the effectiveness of the included RCTs for DKD. The Stata 15.1 and R 4.0.4 were used to perform the network meta-analysis. Sensitivity analysis was used to assess the robustness of the findings. The effect of the intervention evidence are summarized on the basis of the minimum background framework. Results: NMA showed that the total effective rate of SMI, DCI, DHI, HQI, and SKI combined with alprostadil injection (PGE1) was better than PGE1 single used. Based on the surface under the cumulative ranking curve values, PGE1+DHI was the most effective for urinary albumin excretion rate and 24 h urinary albumin, PGE1+HQI was the most effective for the total response rate and β2-MG, and PGE1+SKI was the most effective for serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen. Cluster analysis found that PGE1+HQI and PGE1+SKI could be the best treatments in terms of primary outcome measures. PGE1+SKI was found to be most effective on glomerular filtration function. PGE1+DHI was most effective for urinary protein-related indices. Conclusion: The efficacy of TCMI combined with PGE1 was higher than PGE1 single used. PGE1+HQI and PGE1+SKI were the most effective treatments. The safety of TCMI treatment should be investigated further. This study needs to be validated using large-sample, double-blind, multicentre RCTs. Systematic Review Registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=348333], identifier [CRD42022348333].
Keywords: diabetic kidney disease; injections; network meta-analysis; randomized controlled trial; traditional medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Long, Feng, Liu, Li, Liu, Jiang and Yue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
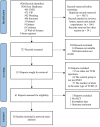
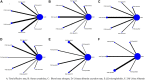

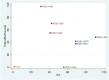
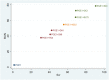
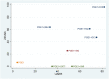
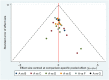
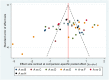
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Chinese Herbal Injections for the Treatment of Primary Nephrotic Syndrome: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 16;11:579241. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.579241. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33178022 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of five different traditional Chinese medicine injections in acute upper respiratory tract infection in children: a network meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Pediatr. 2024 Jun 10;12:1358639. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1358639. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38915872 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of TCMI in Patients With Combined Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 23;12:741261. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.741261. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy of seven Chinese patent medicines for early diabetic kidney disease: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.Complement Ther Med. 2022 Aug;67:102831. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2022.102831. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Complement Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35398481 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine decoction as an adjuvant treatment for diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1327030. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1327030. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bersani-Amado L. E., da Rocha B. A., Schneider L. C. L., Ames F. Q., do Nascimento M. P., Bersani-Amado C. A., et al. (2020). Prostaglandin E1 prevents histopathological changes improving renal function in experimental nephropathy induced by renal microembolism. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 13 (7), 1624–1632. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

