Cancer risks with JAKi and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis: a national real-world cohort study
- PMID: 36868796
- PMCID: PMC10314043
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2022-223636
Cancer risks with JAKi and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis: a national real-world cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Assess cancer risks with Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) versus biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) in clinical practice.
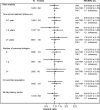
Methods: Cohort study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) initiating treatment with JAKi, tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) or other (non-TNFi) bDMARDs 2016-2020 using prospectively collected data from the Swedish Rheumatology Quality Register linked to other registers including the Cancer Register. We estimated incidence rates, and HRs via Cox regression, for all cancers excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), and for individual cancer types including NMSC.
Results: We identified 10 447 patients with RA and 4443 patients with PsA who initiated treatment with JAKi, a non-TNFi bDMARD or a TNFi. Median follow-up times in RA were 1.95, 2.83 and 2.49 years, respectively. In RA, based on 38 incident cancers other than NMSC with JAKi vs 213 with TNFi the overall HR was 0.94 (95% CI 0.65 to 1.38). Based on 59 vs 189 incident NMSC, the HR was 1.39 (95% CI 1.01 to 1.91). At 2 or more years since treatment start, the HR for NMSC was 2.12 (95% CI 1.15 to 3.89). In PsA, based on 5 vs 73 incident cancers other than NMSC, and 8 vs 73 incident NMSC, the corresponding HRs were 1.9 (95% CI 0.7 to 5.2) and 2.1 (95% CI 0.8 to 5.3).
Conclusion: In clinical practice, the short-term risk of cancer other than NMSC in individuals initiating treatment with JAKi is not higher than for TNFi, but we found evidence of increased risk for NMSC.
Keywords: Arthritis, Psoriatic; Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Biological Therapy; Epidemiology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: VH and KH have no competing interests to declare. JA has had or have research agreements with Abbvie, Astra-Zeneca, BMS, Eli Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, and UCB, mainly in the context of safety monitoring of biologics via ARTIS/Swedish Biologics Register. TF and HB are partly employed by the ARTIS project.
Figures
Comment in
-
In RA, new use of JAK inhibitors was associated with nonmelanoma skin cancer vs. TNF inhibitors at 2 y.Ann Intern Med. 2023 Jul;176(7):JC83. doi: 10.7326/J23-0042. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Ann Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37399557
Similar articles
-
Venous thromboembolism with JAK inhibitors and other immune-modulatory drugs: a Swedish comparative safety study among patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Feb;82(2):189-197. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223050. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 36150749 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative cardiovascular safety with janus kinase inhibitors and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs as used in clinical practice: an observational cohort study from Sweden in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.RMD Open. 2023 Nov 23;9(4):e003630. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003630. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37996125 Free PMC article.
-
Janus kinase inhibitors and tumour necrosis factor inhibitors show a favourable safety profile and similar persistence in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis: real-world data from the BIOBADASER registry.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Aug 27;83(9):1189-1199. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-225271. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38594056
-
[Role of janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of rheumatic diseases].Internist (Berl). 2019 Nov;60(11):1215-1220. doi: 10.1007/s00108-019-00669-z. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31486859 Review. German.
-
Janus kinase versus TNF inhibitors: where we stand today in rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2022 May;18(5):485-493. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2022.2064275. Epub 2022 May 9. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35535405 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer - a dangerous liaison.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1436581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436581. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39359726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK inhibitor selectivity: new opportunities, better drugs?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;20(10):649-665. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01153-1. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39251770 Review.
-
2023 EULAR Recommendations for the Treatment of PsA: Advances and Pending Issues.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2024 Apr 15;35(2):204-206. doi: 10.31138/mjr.050424.ert. eCollection 2024 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39211029 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Biologics or Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Who are Insufficient Responders to Conventional Anti-Rheumatic Drugs.Drugs. 2024 Aug;84(8):877-894. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02059-8. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38949688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biologics Versus JAK Inhibitors. Part I: Cancer Risk. A Narrative Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Jun;14(6):1389-1442. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01166-4. Epub 2024 May 19. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38763966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chakravarty EF, Michaud K, Wolfe F. Skin cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. J Rheumatol 2005;32:2130–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
