Causes, costs and consequences of kinesin motors communicating through the microtubule lattice
- PMID: 36866642
- PMCID: PMC10022682
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.260735
Causes, costs and consequences of kinesin motors communicating through the microtubule lattice
Abstract
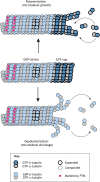
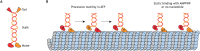
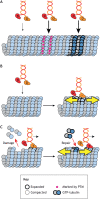
Microtubules are critical for a variety of important functions in eukaryotic cells. During intracellular trafficking, molecular motor proteins of the kinesin superfamily drive the transport of cellular cargoes by stepping processively along the microtubule surface. Traditionally, the microtubule has been viewed as simply a track for kinesin motility. New work is challenging this classic view by showing that kinesin-1 and kinesin-4 proteins can induce conformational changes in tubulin subunits while they are stepping. These conformational changes appear to propagate along the microtubule such that the kinesins can work allosterically through the lattice to influence other proteins on the same track. Thus, the microtubule is a plastic medium through which motors and other microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) can communicate. Furthermore, stepping kinesin-1 can damage the microtubule lattice. Damage can be repaired by the incorporation of new tubulin subunits, but too much damage leads to microtubule breakage and disassembly. Thus, the addition and loss of tubulin subunits are not restricted to the ends of the microtubule filament but rather, the lattice itself undergoes continuous repair and remodeling. This work leads to a new understanding of how kinesin motors and their microtubule tracks engage in allosteric interactions that are critical for normal cell physiology.
Keywords: GTP island; Kinesin; Microtubule; Microtubule lattice; Microtubule repair; Tubulin; Tubulin code.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A kinesin-1 variant reveals motor-induced microtubule damage in cells.Curr Biol. 2022 Jun 6;32(11):2416-2429.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.04.020. Epub 2022 May 2. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35504282 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin-8-specific loop-2 controls the dual activities of the motor domain according to tubulin protofilament shape.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 20;13(1):4198. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31794-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35859148 Free PMC article.
-
Structural model of microtubule dynamics inhibition by kinesin-4 from the crystal structure of KLP-12 -tubulin complex.Elife. 2022 Sep 6;11:e77877. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77877. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36065637 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of kinesin motors, microtubules, and MAPs.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2006;27(2):125-37. doi: 10.1007/s10974-005-9051-4. Epub 2005 Dec 17. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2006. PMID: 16362723 Review.
-
Functional asymmetry in kinesin and dynein dimers.Biol Cell. 2013 Jan;105(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/boc.201200044. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23066835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microtubule-associated protein MAP7 promotes tubulin posttranslational modifications and cargo transport to enable osmotic adaptation.Dev Cell. 2024 Jun 17;59(12):1553-1570.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.03.022. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Dev Cell. 2024. PMID: 38574732
-
Macromolecular Crowding Tailors the Microtubule Cytoskeleton Through Tubulin Modifications and Microtubule-Associated Proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 14:2023.06.14.544846. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544846. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37398431 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Modeling Studies of the Mechanism of Context-Dependent Bidirectional Movements of Kinesin-14 Motors.Molecules. 2024 Apr 15;29(8):1792. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081792. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675612 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin-1-transported liposomes prefer to go straight in 3D microtubule intersections by a mechanism shared by other molecular motors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 16;121(29):e2407330121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407330121. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38980901 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and regulation of kinesin motors.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Feb;26(2):86-103. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00780-6. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39394463 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

