C3a-C3aR signaling is a novel modulator of skeletal homeostasis
- PMID: 36860797
- PMCID: PMC9969257
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2023.101662
C3a-C3aR signaling is a novel modulator of skeletal homeostasis
Abstract
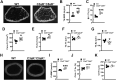
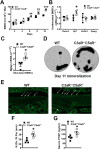
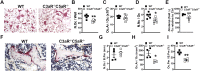
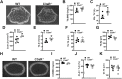
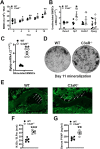
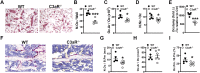
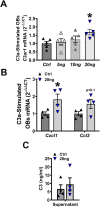
Osteoimmune studies have identified complement signaling as an important regulator of the skeleton. Specifically, complement anaphylatoxin receptors (i.e., C3aR, C5aR) are expressed on osteoblasts and osteoclasts, implying that C3a and/or C5a may be candidate mediators of skeletal homeostasis. The study aimed to determine how complement signaling influences bone modeling/remodeling in the young skeleton. Female C57BL/6J C3aR-/-C5aR-/- vs. wildtype and C3aR-/- vs. wildtype mice were examined at age 10 weeks. Trabecular and cortical bone parameters were analyzed by micro-CT. In situ osteoblast and osteoclast outcomes were determined by histomorphometry. Osteoblast and osteoclast precursors were assessed in vitro. C3aR-/-C5aR-/- mice displayed an increased trabecular bone phenotype at age 10 weeks. In vitro studies revealed C3aR-/-C5aR-/- vs. wildtype cultures had less bone-resorbing osteoclasts and increased bone-forming osteoblasts, which were validated in vivo. To determine whether C3aR alone was critical for the enhanced skeletal outcomes, wildtype vs. C3aR-/- mice were evaluated for osseous tissue outcomes. Paralleling skeletal findings in C3aR-/-C5aR-/- mice, C3aR-/- vs. wildtype mice had an enhanced trabecular bone volume fraction, which was attributed to increased trabecular number. There was elevated osteoblast activity and suppressed osteoclastic cells in C3aR-/- vs. wildtype mice. Furthermore, primary osteoblasts derived from wildtype mice were stimulated with exogenous C3a, which more profoundly upregulated C3ar1 and the pro-osteoclastic chemokine Cxcl1. This study introduces the C3a/C3aR signaling axis as a novel regulator of the young skeleton.
Keywords: Complement; Osteoblast; Osteoclast; Osteoimmunology.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors, Megan B. Kuhn, Hayden S. Vandenburg, Andrew J. Reynolds, Matthew D. Carson, Amy J. Warner, Amanda C. LaRue, Chad M. Novince, and Jessica D. Hathaway-Schrader, declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of the anaphylatoxin receptors, C3aR and C5aR, to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2336-50. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500044. Epub 2016 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26956419 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting C3a/C5a receptors inhibits human mesangial cell proliferation and alleviates immunoglobulin A nephropathy in mice.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Jul;189(1):60-70. doi: 10.1111/cei.12961. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28295247 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell anaphylatoxin receptor expression can enhance IgE-dependent skin inflammation in mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;131(2):541-8.e1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.009. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22728083 Free PMC article.
-
The Complement Receptors C3aR and C5aR Are a New Class of Immune Checkpoint Receptor in Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 19;10:1574. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01574. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31379815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The skeleton in primary hyperparathyroidism: a review focusing on bone remodeling, structure, mass, and fracture.APMIS Suppl. 2001;(102):1-52. APMIS Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11419022 Review.
References
-
- Andrades J.A., Nimni M.E., Becerra J., Eisenstein R., Davis M., Sorgente N. Complement proteins are present in developing endochondral bone and may mediate cartilage cell death and vascularization. Exp. Cell Res. 1996;227(2):208–213. - PubMed
-
- Baxter-Jones A.D., Faulkner R.A., Forwood M.R., Mirwald R.L., Bailey D.A. Bone mineral accrual from 8 to 30 years of age: an estimation of peak bone mass. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011;26(8):1729–1739. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

