A serum miRNAs signature for early diagnosis of bladder cancer
- PMID: 36856518
- PMCID: PMC9980012
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2172206
A serum miRNAs signature for early diagnosis of bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer accounts for the most common type of urologic malignancy and presents high recurrence rate after surgical resection and adjuvant intravesical therapy. We aim to search for an early diagnostic biomarker in serum for bladder cancer in this study.
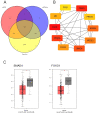
Methods: The expression profiles of miRNAs in serum samples of 112 bladder cancer patients and 112 healthy controls were detected with real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under curve (AUC) analysis were performed to assess the diagnostic efficiency of miRNAs. Stepwise logic regression analysis was used to construct a diagnostic signature with highest sensitivity and specificity. Bioinformatics analysis was applied to explore the potential biological functions and mechanisms of candidate miRNAs.
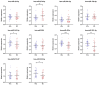
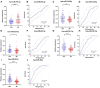
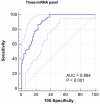
Results: Five miRNAs including miR-451a, miR-381-3p, miR-223-3p, miR-142-5p and miR-27b-3p were found differentially expressed in serum samples of bladder patients and healthy subjects. The diagnostic signature was constructed with miR-27b-3p, miR-381-3p and miR-451a. AUC of the three-miRNA signature was 0.894 (0.837-0.936, p < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of this signature were 86.90% and 77.38%, respectively, indicating that this signature has a good ability to diagnose bladder cancer.
Conclusion: The three-miRNA signature we constructed has favorable diagnostic capacity and may be a promising non-invasive biomarker in the early diagnosis of bladder cancer.KEY MESSAGESThere is still no clinical utilization of serum miRNAs in the early detection of bladder cancer.We screened and constructed a three-miRNA signature with the sensitivity of 86.90% and specificity of 77.38% which may be a promising non-invasive biomarker in the early diagnosis of bladder cancer.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; diagnosis; miRNA; serum biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of a three-miRNA panel in serum for bladder cancer diagnosis by a diagnostic test.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 May;11(5):1005-1016. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-2611. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35706801 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma microRNAs as potential new biomarkers for early detection of early gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 7;25(13):1580-1591. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1580. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30983818 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic panel of serum miR-125b-5p, miR-182-5p, and miR-200c-3p as non-invasive biomarkers for urothelial bladder cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2022 May;24(5):909-918. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02741-3. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35028929
-
Serum microRNA array analysis identifies miR-140-3p, miR-33b-3p and miR-671-3p as potential osteoarthritis biomarkers involved in metabolic processes.Clin Epigenetics. 2017 Dec 12;9:127. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0428-1. eCollection 2017. Clin Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 29255496 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 in urologic cancers: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 23;12:1437951. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1437951. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39114567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Metal-Based Nanomaterials in In Vitro Diagnosis of Tumor Markers: Summary and Prospect.Molecules. 2023 May 26;28(11):4370. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114370. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGR1/LINC00839/SOX5 axis modulates migration, invasion and Gemcitabine resistance of bladder cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2023 Dec 31;24(1):2270106. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2270106. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Cancer Biol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37862152 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing diagnostic signature of serum microRNAs using machine learning for early pan-cancer detection.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jul 4;15(1):263. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01139-1. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38965104 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of an ancillary test for cervical cancer that measures miRNAs and cytokines in serum and cervical mucus.Cancer Sci. 2024 Aug;115(8):2795-2807. doi: 10.1111/cas.16214. Epub 2024 May 15. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38749770 Free PMC article.
-
Screening Model for Bladder Cancer Early Detection With Serum miRNAs Based on Machine Learning: A Mixed-Cohort Study Based on 16,189 Participants.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(20):e70338. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70338. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39440575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Cumberbatch MG, Rota M, Catto JW, et al. . The role of tobacco smoke in bladder and kidney carcinogenesis: a comparison of exposures and meta-analysis of incidence and mortality risks. Eur Urol. 2016;70(3):458–466. - PubMed
-
- DeGeorge KC, Holt HR, Hodges SC.. Bladder cancer: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(8):507–514. - PubMed
-
- Raharja PAR, Hamid ARAH, Mochtar CA, et al. . Recent advances in optical imaging technologies for the detection of bladder cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018;24:192–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
