Patient-Level Pooled Analysis of Ultrasound Renal Denervation in the Sham-Controlled RADIANCE II, RADIANCE-HTN SOLO, and RADIANCE-HTN TRIO Trials
- PMID: 36853627
- PMCID: PMC9975919
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.0338
Patient-Level Pooled Analysis of Ultrasound Renal Denervation in the Sham-Controlled RADIANCE II, RADIANCE-HTN SOLO, and RADIANCE-HTN TRIO Trials
Erratum in
-
Error in Supplement.JAMA Cardiol. 2023 Aug 1;8(8):797. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.1717. JAMA Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37314758 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Ultrasound renal denervation (uRDN) was shown to lower blood pressure (BP) in patients with uncontrolled hypertension (HTN). Establishing the magnitude and consistency of the uRDN effect across the HTN spectrum is clinically important.
Objective: To characterize the effectiveness and safety of uRDN vs a sham procedure from individual patient-level pooled data across uRDN trials including either patients with mild to moderate HTN on a background of no medications or with HTN resistant to standardized triple-combination therapy.
Data sources: A Study of the ReCor Medical Paradise System in Clinical Hypertension (RADIANCE-HTN SOLO and TRIO) and A Study of the ReCor Medical Paradise System in Stage II Hypertension (RADIANCE II) trials.
Study selection: Trials with similar designs, standardized operational implementation (medication standardization and blinding of both patients and physicians to treatment assignment), and follow-up.
Data extraction and synthesis: Pooled analysis using individual patient-level data using linear regression models to compare uRDN with sham across the trials.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was baseline-adjusted change in 2-month daytime ambulatory systolic BP (dASBP) between groups.
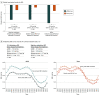
Results: A total of 506 patients were randomized in the 3 studies (uRDN, 293; sham, 213; mean [SD] age, 54.1 [9.3]; 354 male [70.0%]). After a 1-month medication stabilization period, dASBP was similar between the groups (mean [SD], uRDN, 150.3 [9.2] mm Hg; sham, 150.8 [10.5] mm Hg). At 2 months, dASBP decreased by 8.5 mm Hg to mean (SD) 141.8 (13.8) mm Hg among patients treated with uRDN and by 2.9 mm Hg to 147.9 (14.6) mm Hg among patients treated with a sham procedure (mean difference, -5.9; 95% CI, -8.1 to -3.8 mm Hg; P < .001 in favor of uRDN). BP decreases from baseline with uRDN vs sham were consistent across trials and across BP parameters (office SBP: -10.4 mm Hg vs -3.4 mm Hg; mean difference, -6.4 mm Hg; 95% CI, -9.1 to -3.6 mm Hg; home SBP: -8.4 mm Hg vs -1.4 mm Hg; mean difference, -6.8 mm Hg; 95% CI, -8.7 to -4.9 mm Hg, respectively). The BP reductions with uRDN vs sham were consistent across prespecified subgroups. Independent predictors of a larger BP response to uRDN were higher baseline BP and heart rate and the presence of orthostatic hypertension. No differences in early safety end points were observed between groups.
Conclusions and relevance: Results of this patient-level pooled analysis suggest that BP reductions with uRDN were consistent across HTN severity in sham-controlled trials designed with a 2-month primary end point to standardize medications across randomized groups.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02649426 and NCT03614260.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Is There a Role for Renal Denervation in the Treatment of Hypertension?JAMA Cardiol. 2023 May 1;8(5):473-474. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.0372. JAMA Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36853622 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Patient-Level Pooled Analysis of Endovascular Ultrasound Renal Denervation or a Sham Procedure 6 Months After Medication Escalation: The RADIANCE Clinical Trial Program.Circulation. 2024 Mar 5;149(10):747-759. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.066941. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Circulation. 2024. PMID: 37883784 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Renal Denervation vs Sham in Resistant Hypertension After Medication Escalation: Prespecified Analysis at 6 Months of the RADIANCE-HTN TRIO Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Cardiol. 2022 Dec 1;7(12):1244-1252. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2022.3904. JAMA Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36350593 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
12-Month Results From the Unblinded Phase of the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO Trial of Ultrasound Renal Denervation.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Dec 28;13(24):2922-2933. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2020.09.054. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 33357531 Clinical Trial.
-
A Subgroup Meta-Analysis Comparing the Renal Denervation Sham-Controlled Randomized Trials Among Those With Resistant and Nonresistant Hypertension.Am J Cardiol. 2023 Mar 15;191:119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2022.12.032. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Am J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36669381 Review.
-
Renal Denervation for Treating Hypertension: Current Scientific and Clinical Evidence.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019 Jun 24;12(12):1095-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.02.050. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019. PMID: 31221299 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and treatment of obesity-related hypertension-Part 1: Mechanisms.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Nov 13;17(1):sfad282. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad282. eCollection 2024 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38186879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consensus statement on renal denervation by the Joint Committee of Japanese Society of Hypertension (JSH), Japanese Association of Cardiovascular Intervention and Therapeutics (CVIT), and the Japanese Circulation Society (JCS).Hypertens Res. 2024 Oct;47(10):2624-2632. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01700-z. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 39054340
-
Renal denervation in the management of hypertension.EuroIntervention. 2024 Apr 15;20(8):e467-e478. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-23-00836. EuroIntervention. 2024. PMID: 38629418
-
Real-world experience with ultrasound renal denervation utilizing home blood pressure monitoring: the Global Paradise System registry study design.Clin Res Cardiol. 2024 Oct;113(10):1375-1383. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02325-x. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Clin Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37943324 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus statement on renal denervation by the Joint Committee of Japanese Society of Hypertension (JSH), Japanese Association of Cardiovascular Intervention and Therapeutics (CVIT), and the Japanese Circulation Society (JCS).Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2024 Oct;39(4):376-385. doi: 10.1007/s12928-024-01017-1. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2024. PMID: 39080214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azizi M, Sapoval M, Gosse P, et al. ; Renal Denervation for Hypertension (DENERHTN) investigators . Optimum and stepped care andomizedd antihypertensive treatment with or without renal denervation for resistant hypertension (DENERHTN): a multicentre, open-label, andomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;385(9981):1957-1965. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61942-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Azizi M, Schmieder RE, Mahfoud F, et al. ; RADIANCE-HTN Investigators . Endovascular ultrasound renal denervation to treat hypertension (RADIANCE-HTN SOLO): a multicentre, international, single-blind, andomized, sham-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2335-2345. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31082-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

