Oncolytic Avian Reovirus σA-Modulated Upregulation of the HIF-1α/C-myc/glut1 Pathway to Produce More Energy in Different Cancer Cell Lines Benefiting Virus Replication
- PMID: 36851737
- PMCID: PMC9961784
- DOI: 10.3390/v15020523
Oncolytic Avian Reovirus σA-Modulated Upregulation of the HIF-1α/C-myc/glut1 Pathway to Produce More Energy in Different Cancer Cell Lines Benefiting Virus Replication
Abstract
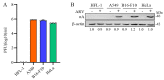
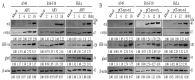
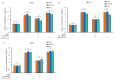
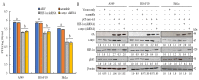
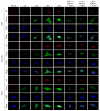
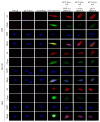
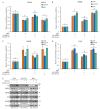
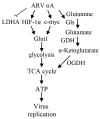
Our previous reports proved that the structural protein σA of avian reovirus (ARV) is an energy activator which can regulate cellular metabolism that is essential for virus replication. This study has further demonstrated that the ARV protein σA is able to upregulate the HIF-1α/myc/glut1 pathway in three cancer cell lines (A549, B16-F10, and HeLa) to alter the metabolic pathway of host cells. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting results have revealed that σA protein could enhance both mRNA and the protein levels of HIF-1α, c-myc, and glut1 in these cancer cell lines. In this work, ATeam immunofluorescence staining was used to reveal that knockdown of HIF-1α, c-myc, and glut1 by shRNAs decreased cellular ATP levels. Our data reveal that the ARV σA protein can downregulate lactate fermentation and upregulate glutaminolysis. The σA protein upregulates glutaminase, which converts glutamate into the TCA cycle intermediate α-ketoglutarate, activating the TCA cycle. In the lactate fermentation pathway, ARV σA protein suppresses lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), implying the Warburg effect does not occur in these cancer cell lines. This study provides a novel finding revealing that ARV σA protein upregulates glycolysis and glutaminolysis to produce energy using the HIF-1α/c-myc/glut1 pathway to benefit virus replication in these cancer cell lines.
Keywords: ATeams; HIF-1α; avian reoviruses; c-myc; glut1; glycolysis; oncolytic virus.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avian reovirus σA-modulated suppression of lactate dehydrogenase and upregulation of glutaminolysis and the mTOC1/eIF4E/HIF-1α pathway to enhance glycolysis and the TCA cycle for virus replication.Cell Microbiol. 2018 Dec;20(12):e12946. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12946. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Cell Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30156372
-
Oncolytic avian reovirus σA-modulated fatty acid metabolism through the PSMB6/Akt/SREBP1/acetyl-CoA carboxylase pathway to increase energy production for virus replication.Vet Microbiol. 2022 Oct;273:109545. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109545. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Vet Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35998542
-
p17-Modulated Hsp90/Cdc37 Complex Governs Oncolytic Avian Reovirus Replication by Chaperoning p17, Which Promotes Viral Protein Synthesis and Accumulation of Viral Proteins σC and σA in Viral Factories.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0007422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00074-22. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35107368 Free PMC article.
-
How does hypoxia inducible factor-1α participate in enhancing the glycolysis activity in cervical cancer?Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013 Jun;17(3):305-11. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23375385 Review.
-
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas.Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jan 26;29(1):71-91. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0032. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28822229 Review.
Cited by
-
Current advances in microbial-based cancer therapies.Med Oncol. 2023 Jun 18;40(7):207. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02074-x. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37330997 Review.
-
The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Tumor Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 20;15(8):2385. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082385. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Entry of Avian Reovirus Modulated by Cell-Surface Annexin A2 and Adhesion G Protein-Coupled Receptor Latrophilin-2 Triggers Src and p38 MAPK Signaling Enhancing Caveolin-1- and Dynamin 2-Dependent Endocytosis.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0000923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00009-23. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37097149 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic viruses-modulated immunogenic cell death, apoptosis and autophagy linking to virotherapy and cancer immune response.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 15;13:1142172. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1142172. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37009515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oncolytic Avian Reovirus p17 Protein Inhibits Invadopodia Formation in Murine Melanoma Cancer Cells by Suppressing the FAK/Src Pathway and the Formation of theTKs5/NCK1 Complex.Viruses. 2024 Jul 17;16(7):1153. doi: 10.3390/v16071153. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066315 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

