Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of the Dynamics of RNA Viruses in Presence of Immunity and Treatment: A Case Study of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36851079
- PMCID: PMC9959189
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11020201
Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of the Dynamics of RNA Viruses in Presence of Immunity and Treatment: A Case Study of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
The emergence of novel RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2 poses a greater threat to human health. Thus, the main objective of this article is to develop a new mathematical model with a view to better understand the evolutionary behavior of such viruses inside the human body and to determine control strategies to deal with this type of threat. The developed model takes into account two modes of transmission and both classes of infected cells that are latently infected cells and actively infected cells that produce virus particles. The cure of infected cells in latent period as well as the lytic and non-lytic immune response are considered into the model. We first show that the developed model is well-posed from the biological point of view by proving the non-negativity and boundedness of model's solutions. Our analytical results show that the dynamical behavior of the model is fully determined by two threshold parameters one for viral infection and the other for humoral immunity. The effect of antiviral treatment is also investigated. Furthermore, numerical simulations are presented in order to illustrate our analytical results.
Keywords: RNA viruses; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral treatment; immunity; mathematical modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
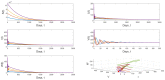
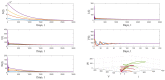
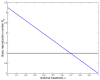
Similar articles
-
Stability of a delayed SARS-CoV-2 reactivation model with logistic growth and adaptive immune response.Physica A. 2023 Apr 15;616:128604. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2023.128604. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Physica A. 2023. PMID: 36909816 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the dynamics of viral infections in presence of latently infected cells.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020 Jul;136:109916. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109916. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020. PMID: 32518473 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 infection model with two modes of transmission and immune response.Math Biosci Eng. 2020 Aug 11;17(5):5326-5340. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020288. Math Biosci Eng. 2020. PMID: 33120555
-
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-specific humoral immunity and its potential applications and therapeutic prospects.Cell Mol Immunol. 2022 Feb;19(2):150-157. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00774-w. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34645940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of green tea catechin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Major interactions with host/virus proteases.Phytomed Plus. 2023 Feb;3(1):100402. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100402. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Phytomed Plus. 2023. PMID: 36597465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of COVID-19 intervention policies using a mathematical model: an optimal control approach.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 4;14(1):494. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50799-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38177230 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of a Fractional-Order Delayed Model of COVID-19 with Vaccination Efficacy.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 29;11(4):758. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11040758. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112670 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine and antiviral drug promise for preventing post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, and their combination for its treatment.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1329162. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1329162. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39185419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- HWO Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19, 21 September 2022. [(accessed on 21 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
-
- Hattaf K., Mohsen A.A., Harraq J., Achtaich N. Modeling the dynamics of COVID-19 with carrier effect and environmental contamination. Int. J. Model. Simul. Sci. Comput. 2021;12:2150048. doi: 10.1142/S1793962321500483. - DOI
-
- Hattaf K., Mohsen A.A. Dynamics of a generalized fractional epidemic model of COVID-19 with carrier effect. Adv. Syst. Sci. Appl. 2022;22:36–48.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

