Current Advances in Lipid Nanosystems Intended for Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications
- PMID: 36839978
- PMCID: PMC9967415
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020656
Current Advances in Lipid Nanosystems Intended for Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
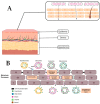
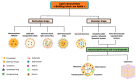
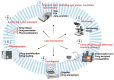
Skin delivery is an exciting and challenging field. It is a promising approach for effective drug delivery due to its ease of administration, ease of handling, high flexibility, controlled release, prolonged therapeutic effect, adaptability, and many other advantages. The main associated challenge, however, is low skin permeability. The skin is a healthy barrier that serves as the body's primary defence mechanism against foreign particles. New advances in skin delivery (both topical and transdermal) depend on overcoming the challenges associated with drug molecule permeation and skin irritation. These limitations can be overcome by employing new approaches such as lipid nanosystems. Due to their advantages (such as easy scaling, low cost, and remarkable stability) these systems have attracted interest from the scientific community. However, for a successful formulation, several factors including particle size, surface charge, components, etc. have to be understood and controlled. This review provided a brief overview of the structure of the skin as well as the different pathways of nanoparticle penetration. In addition, the main factors influencing the penetration of nanoparticles have been highlighted. Applications of lipid nanosystems for dermal and transdermal delivery, as well as regulatory aspects, were critically discussed.
Keywords: dermal delivery; lipid nanosystems; nanoparticles; targeted delivery; transdermal delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overcoming skin barriers through advanced transdermal drug delivery approaches.J Control Release. 2022 Nov;351:361-380. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.025. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36169040 Review.
-
Advancement of Lipid-Based Nanocarriers and Combination Application with Physical Penetration Technique.Curr Drug Deliv. 2019;16(4):312-324. doi: 10.2174/1567201816666190118125427. Curr Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30657039 Review.
-
Topical Drug Delivery of Anti-infectives Employing Lipid-Based Nanocarriers: Dermatokinetics as an Important Tool.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(43):5108-5128. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190118155843. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30657036 Review.
-
(Phospho)lipid-based Nanosystems for Skin Administration.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(29):4174-92. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150901095838. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26323431 Review.
-
Delving Deeper into Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery: Factors and Mechanisms Associated with Nanocarrier-mediated Strategies.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(27):3210-3222. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180924122640. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30246632 Review.
Cited by
-
Prolonged Skin Retention of Luliconazole from SLNs Based Topical Gel Formulation Contributing to Ameliorated Antifungal Activity.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Oct 1;25(7):229. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02945-0. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39354184
-
Editorial on Special Issue "Lipid Nanosystems for Local Drug Delivery".Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 18;15(7):1970. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071970. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514156 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Drug Delivery on Candida Albicans Using Geraniol Nanoemulsion.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 17;15(10):2475. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102475. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896235 Free PMC article.
-
SLNs and NLCs for Skin Applications: Enhancing the Bioavailability of Natural Bioactives.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 28;16(10):1270. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101270. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilizing Silk Sericin as a Biomaterial for Drug Encapsulation in a Hydrogel Matrix with Polycaprolactone: Formulation and Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 16;9(30):32706-32716. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02453. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39100358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sainaga Jyothi V.G.S., Ghouse S.M., Khatri D.K., Nanduri S., Singh S.B., Madan J. Lipid Nanoparticles in Topical Dermal Drug Delivery: Does Chemistry of Lipid Persuade Skin Penetration? J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022;69:103176. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103176. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

