Myelinating Glia: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Polyglutamine Spinocerebellar Ataxias
- PMID: 36831268
- PMCID: PMC9953858
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12040601
Myelinating Glia: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Polyglutamine Spinocerebellar Ataxias
Abstract
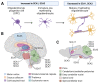
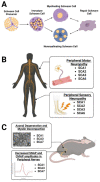
Human studies, in combination with animal and cellular models, support glial cells as both major contributors to neurodegenerative diseases and promising therapeutic targets. Among glial cells, oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells are the myelinating glial cells of the central and peripheral nervous system, respectively. In this review, we discuss the contributions of these central and peripheral myelinating glia to the pathomechanisms of polyglutamine (polyQ) spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) types 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, and 17. First, we highlight the function of oligodendrocytes in healthy conditions and how they are disrupted in polyQ SCA patients and diseased model systems. We then cover the role of Schwann cells in peripheral nerve function and repair as well as their possible role in peripheral neuropathy in polyQ SCAs. Finally, we discuss potential polyQ SCA therapeutic interventions in myelinating glial.
Keywords: Schwann cell; neurodegeneration; oligodendrocyte; peripheral neuropathy; white matter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetics, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Progress in Polyglutamine Spinocerebellar Ataxias.Neurotherapeutics. 2019 Apr;16(2):263-286. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-00696-y. Neurotherapeutics. 2019. PMID: 30607747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Toxicity of Polyglutamine-Expanded TATA-Binding Protein in Glia and Neuronal Cells: Therapeutic Implications for Spinocerebellar Ataxia 17.J Neurosci. 2017 Sep 20;37(38):9101-9115. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0111-17.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 18. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28821675 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Possible Drug Targets in Autosomal Dominant Spinocerebellar Ataxias.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(4):279-293. doi: 10.2174/1871527318666190311155846. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30864514 Review.
-
Polyglutamine spinocerebellar ataxias: emerging therapeutic targets.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Nov;24(11):1099-1119. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1827394. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32962458 Review.
-
Contribution of Glial Cells to Polyglutamine Diseases: Observations from Patients and Mouse Models.Neurotherapeutics. 2023 Jan;20(1):48-66. doi: 10.1007/s13311-023-01357-5. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Neurotherapeutics. 2023. PMID: 37020152 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ASOs are an effective treatment for disease-associated oligodendrocyte signatures in premanifest and symptomatic SCA3 mice.Mol Ther. 2024 May 1;32(5):1359-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.02.033. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38429929
-
The Pattern and Staging of Brain Atrophy in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 2 (SCA2): MRI Volumetrics from ENIGMA-Ataxia.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 17:2024.09.16.613281. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.16.613281. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345594 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Sensitivity of Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Progression over Six Months in Early Spinocerebellar Ataxia.Mov Disord. 2024 Oct;39(10):1856-1867. doi: 10.1002/mds.29934. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Mov Disord. 2024. PMID: 39056163
References
-
- Durr A., Stevanin G., Cancel G., Duyckaerts C., Abbas N., Didierjean O., Chneiweiss H., Benomar A., Lyon-Caen O., Julien J., et al. Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 and Machado-Joseph disease: Clinical, molecular, and neuropathological features. Ann. Neurol. 1996;39:490–499. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390411. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rüb U., Schoels L., Paulson H., Auburger G., Kermer P., Jen J.C., Seidel K., Korf H.W., Deller T. Clinical features, neurogenetics and neuropathology of the polyglutamine spinocerebellar ataxias type 1, 2, 3, 6 and 7. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013;104:38–66. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.01.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

