NbMLP43 Ubiquitination and Proteasomal Degradation via the Light Responsive Factor NbBBX24 to Promote Viral Infection
- PMID: 36831257
- PMCID: PMC9954743
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12040590
NbMLP43 Ubiquitination and Proteasomal Degradation via the Light Responsive Factor NbBBX24 to Promote Viral Infection
Abstract
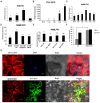
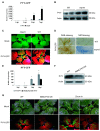
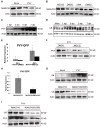
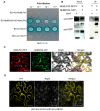
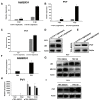
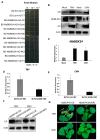
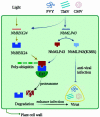
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) plays an important role in virus-host interactions. However, the mechanism by which the UPS is involved in innate immunity remains unclear. In this study, we identified a novel major latex protein-like protein 43 (NbMLP43) that conferred resistance to Nicotiana benthamiana against potato virus Y (PVY) infection. PVY infection strongly induced NbMLP43 transcription but decreased NbMLP43 at the protein level. We verified that B-box zinc finger protein 24 (NbBBX24) interacted directly with NbMLP43 and that NbBBX24, a light responsive factor, acted as an essential intermediate component targeting NbMLP43 for its ubiquitination and degradation via the UPS. PVY, tobacco mosaic virus, (TMV) and cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) infections could promote NbMLP43 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation to enhance viral infection. Ubiquitination occurred at lysine 38 (K38) within NbMLP43, and non-ubiquitinated NbMLP43(K38R) conferred stronger resistance to RNA viruses. Overall, our results indicate that the novel NbMLP43 protein is a target of the UPS in the competition between defense and viral anti-defense and enriches existing theoretical studies on the use of UPS by viruses to promote infection.
Keywords: B-box zinc finger protein 24; MLP-like protein 43; potato virus Y; resistance; ubiquitination; ubiquitin–proteasome system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and functional characterization of NbMLP28, a novel MLP-like protein 28 enhancing Potato virus Y resistance in Nicotiana benthamiana.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Mar 6;20(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01725-7. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32143563 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterially expressed double-stranded RNAs against hot-spot sequences of tobacco mosaic virus or potato virus Y genome have different ability to protect tobacco from viral infection.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010 Nov;162(7):1901-14. doi: 10.1007/s12010-010-8968-2. Epub 2010 May 2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20437276
-
Cucumber mosaic virus infection transiently breaks dsRNA-induced transgenic immunity to Potato virus Y in tobacco.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Oct;16(10):936-44. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.10.936. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 14558695
-
Plant Virus Infection and the Ubiquitin Proteasome Machinery: Arms Race along the Endoplasmic Reticulum.Viruses. 2016 Nov 19;8(11):314. doi: 10.3390/v8110314. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27869775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction of hepatitis B virus with the ubiquitin proteasome system in viral replication and associated pathogenesis.Virol J. 2019 May 30;16(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1183-z. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31146743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the regulatory network of miRNA expression in Potato Y virus-infected of Nicotiana benthamiana using integrated small RNA and transcriptome sequencing.Front Genet. 2024 Jan 8;14:1290466. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1290466. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38259624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y., Yang N., Zheng Y., Yue J., Bhadauria V., Peng Y.-L., Chen Q. Ubiquitination in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae: From development and pathogenicity to stress responses. Phytopathol. Res. 2022;4:1. doi: 10.1186/s42483-021-00106-w. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

