Conformational Analysis of Charged Homo-Polypeptides
- PMID: 36830732
- PMCID: PMC9953673
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13020363
Conformational Analysis of Charged Homo-Polypeptides
Abstract
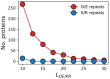
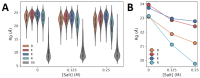
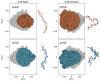
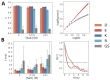
Many proteins have intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs), which are often characterized by a high fraction of charged residues with polyampholytic (i.e., mixed charge) or polyelectrolytic (i.e., uniform charge) characteristics. Polyelectrolytic IDRs include consecutive positively charged Lys or Arg residues (K/R repeats) or consecutive negatively charged Asp or Glu residues (D/E repeats). In previous research, D/E repeats were found to be about five times longer than K/R repeats and to be much more common in eukaryotes. Within these repeats, a preference is often observed for E over D and for K over R. To understand the greater prevalence of D/E over K/R repeats and the higher abundance of E and K, we simulated the conformational ensemble of charged homo-polypeptides (polyK, polyR, polyD, and polyE) using molecular dynamics simulations. The conformational preferences and dynamics of these polyelectrolytic polypeptides change with changes in salt concentration. In particular, polyD and polyE are more sensitive to salt than polyK and polyR, as polyD and polyE tend to adsorb more divalent cations, which leads to their having more compact conformations. We conclude with a discussion of biophysical explanations for the relative abundance of charged amino acids and particularly for the greater abundance of D/E repeats over K/R repeats.
Keywords: D/E repeats; K/R repeats; intrinsically disordered proteins; molecular dynamics simulations; polyelectrolytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Negatively Charged Disordered Regions are Prevalent and Functionally Important Across Proteomes.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jul 30;434(14):167660. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167660. Epub 2022 May 31. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35659505
-
Negatively charged, intrinsically disordered regions can accelerate target search by DNA-binding proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 9;51(10):4701-4712. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad045. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36774964 Free PMC article.
-
Conformations of intrinsically disordered proteins are influenced by linear sequence distributions of oppositely charged residues.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 13;110(33):13392-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304749110. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23901099 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of Electrostatic Charges in Compactness, Aggregation, and Phase Separation of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6208. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176208. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of macromolecules in the formation of kidney stones.Urolithiasis. 2017 Feb;45(1):57-74. doi: 10.1007/s00240-016-0948-8. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Urolithiasis. 2017. PMID: 27913854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Per Aspera ad Chaos: Vladimir Uversky's Odyssey through the Strange World of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 19;13(6):1015. doi: 10.3390/biom13061015. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

