Action Mechanism of Metformin and Its Application in Hematological Malignancy Treatments: A Review
- PMID: 36830619
- PMCID: PMC9953052
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13020250
Action Mechanism of Metformin and Its Application in Hematological Malignancy Treatments: A Review
Abstract
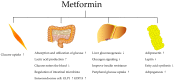
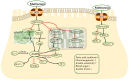
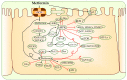
Hematologic malignancies (HMs) mainly include acute and chronic leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma and other heterogeneous tumors that seriously threaten human life and health. The common effective treatments are radiotherapy, chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), which have limited options and are prone to tumor recurrence and (or) drug resistance. Metformin is the first-line drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Recently, studies identified the potential anti-cancer ability of metformin in both T2DM patients and patients that are non-diabetic. The latest epidemiological and preclinical studies suggested a potential benefit of metformin in the prevention and treatment of patients with HM. The mechanism may involve the activation of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway by metformin as well as other AMPK-independent pathways to exert anti-cancer properties. In addition, combining current conventional anti-cancer drugs with metformin may improve the efficacy and reduce adverse drug reactions. Therefore, metformin can also be used as an adjuvant therapeutic agent for HM. This paper highlights the anti-hyperglycemic effects and potential anti-cancer effects of metformin, and also compiles the in vitro and clinical trials of metformin as an anti-cancer and chemosensitizing agent for the treatment of HM. The need for future research on the use of metformin in the treatment of HM is indicated.
Keywords: AMPK; leukemia; lymphoma; metformin; myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research Progress on the Use of Metformin in Leukemia Treatment.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024 Feb;25(2):220-236. doi: 10.1007/s11864-024-01179-3. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38286894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin as a therapeutic tool for resistant hematological malignancies: a literature review.Chin Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun;13(3):39. doi: 10.21037/cco-23-157. Epub 2024 May 24. Chin Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38859606 Review.
-
Repurposing Metformin in hematologic tumor: State of art.Curr Probl Cancer. 2023 Aug;47(4):100972. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2023.100972. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Curr Probl Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37364455 Review.
-
[Antitumor mechanism of metformin via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013 Aug 20;16(8):427-32. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2013.08.07. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23945247 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Mechanism and application of metformin in kidney diseases: An update.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111454. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111454. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33714781 Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin: A Dual-Role Player in Cancer Treatment and Prevention.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 6;25(7):4083. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074083. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Metformin on the Development of Hypothyroidism and Cardiotoxicity Induced by Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate, and Fluorouracil in Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 16;16(9):1312. doi: 10.3390/ph16091312. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765120 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology-based investigation and experimental validation of the mechanism of metformin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Sep 30;29(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02022-z. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39343915 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of Chronically Used Drugs in Cancer Therapy: A Chance to Grasp.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;15(12):3199. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123199. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and risk of hematological cancers in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Saudi Med. 2024 Mar-Apr;44(2):126-134. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2024.126. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Ann Saudi Med. 2024. PMID: 38615182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu J., Bell C., Campbell V., DeBacker J., Tamberg E., Lee C., Mehta S. Noninvasive Ventilation in Patients With Hematologic Malignancy. J. Intensive Care Med. 2017:885066617690725. - PubMed
-
- Al-Dorzi H.M., Al Orainni H., Al Eid F., Tlayjeh H., Itani A., Al Hejazi A., Arabi Y.M. Characteristics and predictors of mortality of patients with hematologic malignancies requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2017;12:259–265. doi: 10.4103/atm.ATM_21_17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

