Effects of T3 Administration on Ex Vivo Rat Hearts Subjected to Normothermic Perfusion: Therapeutic Implications in Donor Heart Preservation and Repair
- PMID: 36824295
- PMCID: PMC9941138
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2023.10742
Effects of T3 Administration on Ex Vivo Rat Hearts Subjected to Normothermic Perfusion: Therapeutic Implications in Donor Heart Preservation and Repair
Abstract
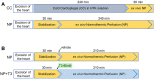
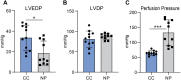
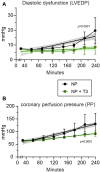
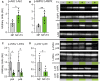
The present study investigated the effects of triiodothyronine (T3) administration in ex vivo model of rat heart normothermic perfusion. T3 is cardioprotective and has the potential to repair the injured myocardium. Isolated hearts were subjected to normothermic perfusion (NP) with Krebs-Henseleit for 4 h with vehicle (NP) or 60 nM T3 in the perfusate (NP + T3). Left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP), left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP), perfusion pressure (PP) and percentage of change of these parameters from the baseline values were measured. Activation of stress induced kinase signaling was assessed in tissue samples. Baseline parameters were similar between groups. LVEDP was increased from the baseline by 13% (70) for NP + T3 vs. 139% (160) for NP group, p = 0.048. LVDP was reduced by 18.2% (5) for NP + T3 vs. 25.3% (19) for NP group, p = 0.01. PP was increased by 41% (19) for NP + T3 vs.91% (56) for NP group, p = 0.024. T3 increased activation of pro-survival Akt by 1.85 fold (p = 0.047) and AMPK by 2.25 fold (p = 0.01) and reduced activation of pro-apoptotic p38 MAPK by 3fold (p = 0.04) and p54 JNK by 4.0 fold (p = 0.04). Administration of T3 in normothermic perfusion had favorable effects on cardiac function and perfusion pressure and switched death to pro-survival kinase signaling.
Keywords: cold cardioplegia; heart; kinase signalling; normothermic perfusion; thyroid hormone.
Copyright © 2023 Mourouzis, Kounatidis, Brozou, Anagnostopoulos, Katsaouni, Lourbopoulos and Pantos.
Conflict of interest statement
The following patent is relevant to the work in this manuscript: PCT/4972/2021. Pharmaceutical composition comprising L-triiodothyronine (T3) for use in the treatment of tissue hypoxia and sepsis. CP and IM are the inventors and hold royalties in relation to this patent. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preservation by cold storage vs ex vivo normothermic perfusion of marginal donor hearts: clinical, histopathologic, and ultrastructural features.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Dec;39(12):1408-1416. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2020.08.021. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33041182
-
A whole blood-based perfusate provides superior preservation of myocardial function during ex vivo heart perfusion.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015 Jan;34(1):113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2014.09.021. Epub 2014 Sep 28. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25447577
-
Triiodothyronine concomitantly inhibits calcium overload and postischemic myocardial stunning in diabetic rats.Life Sci. 2001 Sep 7;69(16):1907-18. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01274-7. Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11693271
-
Normothermic donor heart perfusion: current clinical experience and the future.Transpl Int. 2015 Jun;28(6):634-42. doi: 10.1111/tri.12361. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Transpl Int. 2015. PMID: 24853906 Review.
-
Ex vivo normothermic perfusion in heart transplantation: a review of the TransMedics® Organ Care System.Future Cardiol. 2022 Jan;18(1):5-15. doi: 10.2217/fca-2021-0030. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Future Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34503344 Review.
Cited by
-
Donor Heart Preservation: Current Knowledge and the New Era of Machine Perfusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 24;24(23):16693. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316693. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khush KK, Cherikh WS, Chambers DC, Harhay MO, Hayes D, Jr., Hsich E, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-Sixth Adult Heart Transplantation Report - 2019; Focus Theme: Donor and Recipient Size Match. J Heart Lung Transpl (2019) 38(10):1056–66. 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

