Probiotic-educated Tregs are more potent than naïve Tregs for immune tolerance in stressed new-born mice
- PMID: 36815493
- PMCID: PMC10124588
- DOI: 10.3920/BM2022.0095
Probiotic-educated Tregs are more potent than naïve Tregs for immune tolerance in stressed new-born mice
Abstract
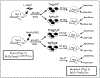
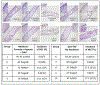
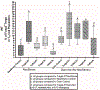
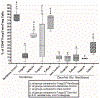
When new-born mice are subjected to acute maternal separation stress, cow-milk based formula feeding, and brief recurrent hypoxia with cold stress, they develop gut inflammation similar to the phenotype of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis, characterised by an increase in gut mucosal effector T (Teffs) and reduced Foxp3+ regulatory T (Tregs) cells. The imbalance can be prevented by probiotic Limosilactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 (LR 17938). We hypothesised that LR 17938 could potentiate a tolerogenic function of Tregs. To analyse whether LR 17938 can educate Tregs to improve their tolerogenic potency during neonatal stress, we isolated T cells (Tregs and Teffs) from 'donor' mice fed with either LR 17938 (107 cfu) or control media. The cells were adoptively transferred (AT) by intraperitoneal injection (5 × 105 cells/mouse) to new-born (d5) recipient mice. Mice were then separated from their dams, fed formula by gavage, and exposed to hypoxia and cold stress (NeoStress) for 4 days. We analysed the percentage of Tregs in CD4+T helper cells in the intestine (INT) and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) of recipient mice. We found that: (1) the percentage of Tregs in the INT and MLN following NeoStress were significantly reduced compared to dam-fed unstressed mice; (2) AT of either naïve Tregs or LR-educated Tregs to mice with Neostress increased the percentage of Tregs in the INT and MLN compared to the percentage in NeoStress mice without Treg treatment; however, LR-educated Tregs increased the Tregs significantly more than naïve Tregs; and (3) AT of LR-educated Tregs reduced pro-inflammatory CD44+Foxp3-NonTregs and inflammatory CX3CR1+ dendritic cells in the intestinal mucosa of NeoStress mice. In conclusion, adoptive transfer of Tregs promotes the generation of and/or migration of endogenous Tregs in the intestinal mucosa of recipient mice. Importantly, probiotic-educated Tregs are more potent than naïve Tregs to enhance immune tolerance following neonatal stress.
Keywords: Limosilactobacillus reuteri; adoptive transfer; immune tolerance; intestinal mucosa; maternal separation; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 changes the frequency of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the intestine and mesenteric lymph node in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056547. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437165 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 against experimental necrotizing enterocolitis is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Aug 1;315(2):G231-G240. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00084.2017. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29648878 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 differentially modulates effector memory T cells and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in a mouse model of necrotizing enterocolitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Jul 15;307(2):G177-86. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00038.2014. Epub 2014 May 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24852566 Free PMC article.
-
Human Breast Milk Promotes the Immunomodulatory Function of Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 in the Neonatal Rat Intestine.J Probiotics Health. 2019;7(1):210. doi: 10.35248/2329-8901.19.7.210. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Probiotics Health. 2019. PMID: 31565666 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 feeding of healthy newborn mice regulates immune responses while modulating gut microbiota and boosting beneficial metabolites.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Dec 1;317(6):G824-G838. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00107.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31482733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Probiotic Limosilactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 Changes Foxp3 Deficiency-Induced Dyslipidemia and Chronic Hepatitis in Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 12;16(4):511. doi: 10.3390/nu16040511. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398835 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus reuteri in digestive system diseases: focus on clinical trials and mechanisms.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 18;13:1254198. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1254198. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37662007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cerny V, Petraskova P, Novotna O, Borakova K, Prokesova L, Kolarova L and Hrdy J, 2020. Value of cord blood Treg population properties and function-associated characteristics for predicting allergy development in childhood. Cent Eur J Immunol 45: 393–402. 10.5114/ceji.2020.103413 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

