Association of inflammation and cognition in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36815174
- PMCID: PMC9939705
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1069439
Association of inflammation and cognition in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The development of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) may be associated with an inflammatory process. Inflammatory cytokines may be a surrogate for systemic inflammation leading to worsening neurological function. We aim to investigate the association between cognitive impairment and inflammation by pooling and analyzing the data from previously published studies.
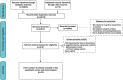
Methods: We performed a systematic literature search on MEDLINE, PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Scopus for prospective longitudinal and cross-sectional studies evaluating the relationship between inflammation and cognitive functions.
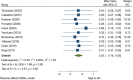
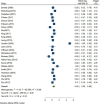
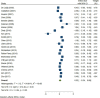
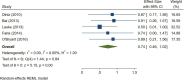
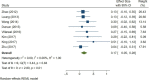
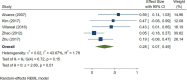
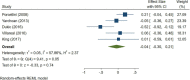
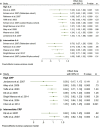
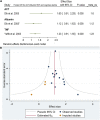
Results: A total of 79 articles were included in our systematic review and meta-analysis. Pooled estimates from cross-sectional studies have demonstrated an increased level of C-reactive protein (CRP) [Hedges's g 0.35, 95% CI (0.16, 0.55), p < 0.05], IL-1β [0.94, 95% CI (-0.04, 1.92), p < 0.05], interleukin-6 (IL-6) [0.46, 95% CI (0.05, 0.88), p < 0.005], TNF alpha [0.22, 95% CI (-0.24, 0.68), p < 0.05], sTNFR-1 [0.74, 95% CI (0.46, 1.02), p < 0.05] in AD compared to controls. Similarly, higher levels of IL-1β [0.17, 95% CI (0.05, 0.28), p < 0.05], IL-6 [0.13, 95% CI (0.08, 0.18), p < 0.005], TNF alpha [0.28, 95% CI (0.07, 0.49), p < 0.05], sTNFR-1 [0.21, 95% CI (0.05, 0.48), p < 0.05] was also observed in MCI vs. control samples. The data from longitudinal studies suggested that levels of IL-6 significantly increased the risk of cognitive decline [OR = 1.34, 95% CI (1.13, 1.56)]. However, intermediate levels of IL-6 had no significant effect on the final clinical endpoint [OR = 1.06, 95% CI (0.8, 1.32)].
Conclusion: The data from cross-sectional studies suggest a higher level of inflammatory cytokines in AD and MCI as compared to controls. Moreover, data from longitudinal studies suggest that the risk of cognitive deterioration may increase by high IL-6 levels. According to our analysis, CRP, antichymotrypsin (ACT), Albumin, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha may not be good surrogates for neurological degeneration over time.
Keywords: CRP; IL-6; cognition; cytokines; elderly; inflammation.
Copyright © 2023 Leonardo and Fregni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inflammatory markers in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis and systematic review of 170 studies.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019 May;90(5):590-598. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-319148. Epub 2019 Jan 10. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30630955
-
Peripheral high levels of CRP predict progression from normal cognition to dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Neurosci. 2023 Jan;107:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2022.11.016. Epub 2022 Dec 8. J Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36502782 Review.
-
Peripheral levels of C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β across the mood spectrum in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of mean differences and variability.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Oct;97:193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.07.014. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 34332041
-
The relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and cognitive dysfunction in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 8;121:110668. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2022.110668. Epub 2022 Oct 23. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36283512 Review.
-
Peripheral inflammation in mild cognitive impairment with possible and probable Lewy body disease and Alzheimer's disease.Int Psychogeriatr. 2019 Apr;31(4):551-560. doi: 10.1017/S1041610218001126. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Int Psychogeriatr. 2019. PMID: 30854988
Cited by
-
New insights on the link between Epstein‑Barr virus infection and cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2024 Aug 30;28(5):413. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12702. eCollection 2024 Nov. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39268367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasudil attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment in C57BL/6 mice through anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects: Possible role of aquaporin-4.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;17:372-381. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.10.004. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39534317 Free PMC article.
-
A perspective on the role of physiological stresses in cancer, diabetes and cognitive disease as environmental diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 20;10:1274221. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1274221. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38053578 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Cytokines and Cognition in Alzheimer's Disease and Its Prodrome.Psychiatry Investig. 2024 Oct;21(10):1054-1064. doi: 10.30773/pi.2024.0071. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Psychiatry Investig. 2024. PMID: 39465234 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα polymorphisms and longitudinal trajectories of cognitive function in non-demented older adults.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Jun 29;39:100816. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100816. eCollection 2024 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39055623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashraf-Ganjouei A., Moradi K., Bagheri S., Aarabi M. (2020). The association between systemic inflammation and cognitive performance in healthy adults. J. Neuroimmunol. 345:577272. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

