Transcription Activation of Rab8A by PEA3 Augments Progression of Esophagus Cancer by Activating the Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36815135
- PMCID: PMC9940983
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/8143581
Transcription Activation of Rab8A by PEA3 Augments Progression of Esophagus Cancer by Activating the Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: Rab8A has been reported as an oncogenic gene in breast and cervical cancer. However, the function and molecular mechanism of Rab8A in esophagus cancer has not been reported.
Methods: Rab8A expression was detected by qPCR and western blotting assays, small interference RNA (siRNA) was applied to reduce Rab8A expression, and the biological behaviors of esophagus cancer cells were estimated by cell counting kit-8, colony formation, and transwell and western blotting assays. The transcriptional factor of Rab8A was verified by dual-luciferase assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. The protein expression of key genes in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was determined by western blotting assay. M435-1279 was used to suppress the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
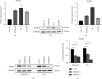
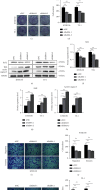
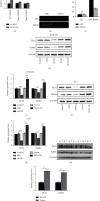
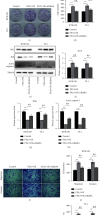
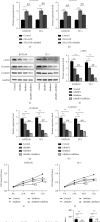
Results: A significant increase of Rab8A expression has been found in esophagus cancer cells. Knockdown of Rab8A suppressed the viability, colony formation, migration, and invasion abilities of esophagus cancer cells and induced apoptosis. PEA3 transcriptionally regulated Rab8A expression and promoted the viability, colony formation, migration, and invasion abilities of esophagus cancer cells and blocked apoptosis, which were diminished by si-Rab8A transfection. Additionally, the expression levels of key genes related to the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway were strengthened by PEA3 overexpression, which were reduced by si-Rab8A transfection. M435-1279 treatment significantly reduced the viability and colony formation of esophagus cancer cells.
Conclusions: The data showed that Rab8A was transcriptionally regulated by PEA3 and promoted the malignant behaviors of esophagus cancer cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The above results indicated that Rab8A may be considered as a promising biomarker for diagnosis and precision treatment in esophagus cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Shusheng Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing EPHB2 diminished the malignant biological properties of esophagus cancer cells by blocking autophagy and Wnt/β-catenin pathway.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Oct;38(10):e23853. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23853. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39291656
-
SAFB2 Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway via NFAT5.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;65(9):1465-1475. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00649-z. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36652182
-
PARG Promotes Esophagus Cancer Cell Metastasis by Activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Biochem Genet. 2024 Apr;62(2):761-774. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10434-5. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37429965
-
MicroRNA-140 Represses Esophageal Cancer Progression via Targeting ZEB2 to Regulate Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.J Surg Res. 2021 Jan;257:267-277. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.07.074. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 32862055
-
Forkhead Box S1 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to regulate colorectal cancer progression.J Transl Med. 2022 Jul 21;20(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03525-1. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35864528 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circular RNAs and cervical cancer: friends or foes? A landscape on circRNA-mediated regulation of key signaling pathways involved in the onset and progression of HPV-related cervical neoplasms.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 10;22(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01494-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38341592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

