High-quality genome of Diaphanosoma dubium provides insights into molecular basis of its broad ecological adaptation
- PMID: 36798432
- PMCID: PMC9926121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106006
High-quality genome of Diaphanosoma dubium provides insights into molecular basis of its broad ecological adaptation
Abstract
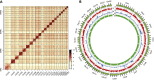
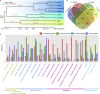
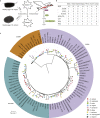
Diaphanosoma dubium Manuilova, 1964, is a widespread planktonic water flea in Asian freshwater. Although sharing similar ecological roles with species of Daphnia, studies on D. dubium and its congeners are still few and lacking a genome for the further studies. Here, we assembled a high quality and chromosome level genome of D. dubium by combining long reads sequencing and Hi-C technologies. The total length of assembled genome was 101.8 Mb, with 98.92 Mb (97.2%) anchored into 22 chromosomes. Through comparative genomic analysis, we found the genes, involved in anti-ROS, detoxification, protein digestion, germ cells regulation and protection, underwent expansion in D. dubium. These genes and their expansion helpfully explain its widespread geographical distribution and dominance in eutrophic waters. This study provides insight into the adaptive evolution of D. dubium at genomic perspectives, and the present high quality genomic resource will be a footstone for future omics studies of the species and its congeners.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Evolutionary biology; Genomics.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
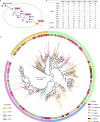
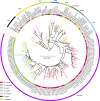
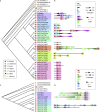
Similar articles
-
The mitochondrial genome of Diaphanosoma dubium with comparison with Daphnia magna.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2017 Dec 8;2(2):926-927. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2017.1413295. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2017. PMID: 33474039 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of burbot (Lota lota) provides insights into the evolutionary adaptations in freshwater.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021 Aug;21(6):2022-2033. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13382. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021. PMID: 33730415
-
Complete mitochondrial DNA of the marine water flea Diaphanosoma celebensis (Cladocera, Sididae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020 Jun 1;5(3):2254-2255. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1772138. eCollection 2020. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020. PMID: 33366996 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level de novo genome assembly of Sarcophaga peregrina provides insights into the evolutionary adaptation of flesh flies.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021 Jan;21(1):251-262. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13246. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021. PMID: 32853451
-
The genome of the freshwater water flea Daphnia magna: A potential use for freshwater molecular ecotoxicology.Aquat Toxicol. 2019 May;210:69-84. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.02.009. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Aquat Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30826642
References
-
- Ebert D. National Library of Medicine; 2005. Ecology, Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia.
-
- Chaturvedi A., Zhou J., Raeymaekers J.A.M., Czypionka T., Orsini L., Jackson C.E., Spanier K.I., Shaw J.R., Colbourne J.K., De Meester L. Extensive standing genetic variation from a small number of founders enables rapid adaptation in Daphnia. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:4306. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24581-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

