Cardiovascular Toxicities Associated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 36795308
- PMCID: PMC10392782
- DOI: 10.1007/s11886-023-01845-2
Cardiovascular Toxicities Associated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
Purpose of review: To provide a detailed overview of cardiovascular adverse events associated with the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors across different tumor types.
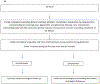
Recent findings: Despite an undeniable survival advantage of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with hematologic or solid malignancies, the accompanying off-target cardiovascular adverse events can be life-threatening. In patients with B cell malignancies, the use of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors has been associated with atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, as well as hypertension. Cardiovascular toxic profiles are heterogeneous among the several approved breakpoint cluster region (BCR)-ABL TKIS. Notably, imatinib might be cardioprotective. Vascular endothelial growth factor TKIs, constituting the central axis in the treatment of several solid tumors, including renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, have strongly been associated with hypertension and arterial ischemic events. Epidermal growth factor TKIs as therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have been reported to be infrequently associated with heart failure and QT prolongation. While tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been demonstrated to increase overall survival across different types of cancers, special consideration should be given to cardiovascular toxicities. High-risk patients can be identified by undergoing a comprehensive workup at baseline.
Keywords: BCR-ABL; Bruton tyrosine kinase; Cardiovascular toxicity; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-associated cardiovascular adverse events in chronic myeloid leukemia].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2021;62(8):1024-1028. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.62.1024. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2021. PMID: 34497188 Japanese.
-
Assessment of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Survival and Cardiovascular Outcomes of Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Taiwan.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 May 1;6(5):e2313824. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13824. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37195663 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular diseases in patients receiving small molecules with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor activity: A meta-analysis of approximately 29,000 cancer patients.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2018 Mar;25(5):482-494. doi: 10.1177/2047487318755193. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29376753 Review.
-
Efficacy of Next-Generation EGFR-TKIs in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820940426. doi: 10.1177/1533033820940426. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32723164 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary complications of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Eur Respir J. 2020 Oct 29;56(4):2000279. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00279-2020. Print 2020 Oct. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32527740 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular Toxicity in Cancer Therapy: Protecting the Heart while Combating Cancer.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024 Sep;26(9):953-971. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02099-2. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39042344 Review.
-
Imatinib‑ and ponatinib‑mediated cardiotoxicity in zebrafish embryos and H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):187. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13311. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39219269 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Adverse Events of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Clinical Relevance, Impact on Outcome, Preventive Measures and Treatment Strategies.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023 Dec;24(12):1720-1738. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01149-1. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38047977 Review.
-
Depletion of lncRNA MEG3 Ameliorates Imatinib-Induced Injury of Cardiomyocytes via Regulating miR-129-5p/HMGB1 Axis.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023 Nov 17;2023:1108280. doi: 10.1155/2023/1108280. eCollection 2023. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 38028435 Free PMC article.
-
Triple targeting of RSK, AKT, and S6K as pivotal downstream effectors of PDPK1 by TAS0612 in B-cell lymphomas.Cancer Sci. 2023 Dec;114(12):4691-4705. doi: 10.1111/cas.15995. Epub 2023 Oct 15. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37840379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Treon SP, Tripsas CK, Meid K, et al. Ibrutinib in previously treated Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(15):1430–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

