LncRNA PCAT6 promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cell by targeting miR-545-3p
- PMID: 36787056
- PMCID: PMC10042954
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-023-08259-x
LncRNA PCAT6 promotes proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cell by targeting miR-545-3p
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is a high incidence cancer on a worldwide basis and has become a major public health problem. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) makes up approximately half of all lung cancers and is a threat to human health. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) is an important regulator of the development and progression of lung adenocarcinoma. In this manuscript we examined the role and potential mechanism of lncRNA PCAT6 in the development of LUAD.
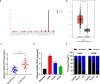
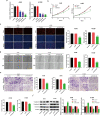
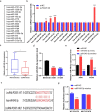
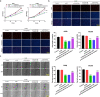
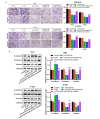
Methods and results: Differences in lncRNA PCAT6 levels between LUAD samples and normal samples were first explored in the GEPIA database. We found that lncRNA PCAT6 expression was elevated, which was also validated in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and cell lines. Using western blotting, CCK-8, EdU, wound healing and transwell assays, we found that knockdown of lncRNA PCAT6 inhibited EMT, proliferation, migration, and invasion of LUAD cells. We noted a predicted a binding site for lncRNA PCAT6 and miR-545-3p through conducting bioinformatic analyses, and their binding was subsequently verified by a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Rescue experiments confirmed that miR-545-3p inhibitor partially abolished the inhibition function of lncRNA PCAT6 knockdown on LUAD cells. In addition, we predicted the downstream target genes of miR-545-3p and verified them by RT-qPCR. We found that EGFR was reduced in the silence of lncRNA PCAT6 and upregulated after miR-545-3p inhibition.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that lncRNA PCAT6 promotes a more aggressive LUAD phenotype by sponging miR-545-3p. This finding may provide new ideas for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: EMT; Lung adenocarcinoma; lncRNA PCAT6; miR-545- 3p.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression and clinical significance of long non-coding RNAs in the development and progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 6;14:1411672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1411672. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38912059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA FAM83A antisense RNA 1 (lncRNA FAM83A-AS1) targets microRNA-141-3p to regulate lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):4964-4977. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037871. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35164653 Free PMC article.
-
Novel long non-coding RNA LINC02323 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via sponging miR-1343-3p in lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Sep;11(9):2506-2516. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13562. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32643848 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SGMS1-AS1 regulates lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT progression via miR-106a-5p/MYLI9 axis.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Jul;12(14):2104-2112. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14043. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34061466 Free PMC article.
-
Functions, mechanisms, and clinical applications of lncRNA LINC00857 in cancer pathogenesis.Hum Cell. 2023 Sep;36(5):1656-1671. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00936-0. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 37378889 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs in lung cancer: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 8;13:1256537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1256537. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37746261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances on high-efficiency of microRNAs in different types of lung cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 20;23(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03133-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37986065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a novel signature to predict prognosis and immune characteristics of pancreatic cancer based on necroptosis-related long non-coding RNA.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Sep;50(9):7405-7419. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08663-3. Epub 2023 Jul 15. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37452900
-
Low expression of Lnc-ENST00000535078 inhibits the migration, invasion, and enhances apoptosis of CTPE-induced malignantly transformed BEAS-2B cells.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Aug 21;13(4):tfae121. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae121. eCollection 2024 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39175813
-
Differential expression and clinical significance of long non-coding RNAs in the development and progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 6;14:1411672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1411672. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38912059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim N, Kim HK, Lee K, Hong Y, Cho JH, Choi JW, Lee JI, Suh YL, Ku BM, Eum HH, Choi S, Choi YL, Joung JG, Park WY, Jung HA, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K, Ahn MJ, Lee HO. Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2285. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16164-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

