Pharmaceutical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of a newly formulated multiparticulate matrix of levodopa and carbidopa
- PMID: 36778908
- PMCID: PMC9909728
- DOI: 10.5599/admet.1474
Pharmaceutical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of a newly formulated multiparticulate matrix of levodopa and carbidopa
Abstract
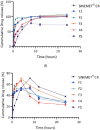
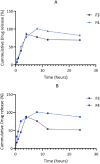
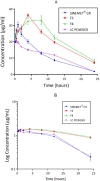
Levodopa is routinely co-administered with carbidopa in the management of Parkinson's disease. Although the aforementioned combination therapy is effective, there may be fluctuating plasma levels of levodopa after oral administration. We formulated and evaluated the kinetic characteristics of the chitosan-pectin-based multiparticulate matrix of levodopa and carbidopa. Pectin was extracted from the cocoa husk, and the chitosan-pectin-based matrix was prepared by wet granulation. Formulations were evaluated for drug-excipient compatibility, drug content, precompression properties and in vitro release. For pharmacokinetic evaluation, rats were put into groups and administered either chitosan-pectin based matrix of levodopa/carbidopa, Sinemet® CR or levodopa/carbidopa immediate release powder. Rats were administered the different formulations of levodopa/carbidopa (20/5 mg/kg) per os every 12 hours. The pharmacokinetic parameters of levodopa were estimated for the various treatment groups. The percentage content of levodopa and carbidopa in the various formulations was within the acceptance criteria. The AUC0-24 for levodopa/carbidopa multiparticulate matrix (Formulation 3: 484.98 ± 18.70 μg.hr/mL); Formulation 4: 535.60 ± 33.04 μg.hr/mL), and Cmax (Formulation 3: 36.28 ± 1.52 μg/mL; Formulation 4: 34.80 ± 2.19 μg/mL) were higher than Sinemet® CR (AUC0-24 262.84 ± 16.73 μg.hr/mL and Cmax 30.62 ± 3.37 μg/mL). The t 1/2 of the new formulation was longer compared to Sinemet® CR.
Keywords: Chitosan; Formulation; Management; Parkinson’s disease; Pectin; Pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2022 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chitosan-Coated Hydroxypropylmethyl Cellulose Microparticles of Levodopa (and Carbidopa): In Vitro and Rat Model Kinetic Characteristics.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2020 Nov 3;93:100612. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2020.100612. eCollection 2020. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2020. PMID: 33296447 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of an oral extended-release capsule formulation of carbidopa-levodopa (IPX066) with immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet(®)), sustained-release carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet(®) CR), and carbidopa-levodopa-entacapone (Stalevo(®)).J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;55(9):995-1003. doi: 10.1002/jcph.514. Epub 2015 May 20. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25855267 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a Pectin-Based Oral Multiparticulate Matrix Carrier of Carbamazepine.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021 Jul 3;2021:5527452. doi: 10.1155/2021/5527452. eCollection 2021. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34286279 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical design and development of a Sinemet controlled-release formulation.Neurology. 1989 Nov;39(11 Suppl 2):20-4. Neurology. 1989. PMID: 2685648 Review.
-
Clinical studies with and pharmacokinetic considerations of sustained-release levodopa.Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1 Suppl 1):29-32; discussion 57-60. Neurology. 1992. PMID: 1549198 Review.
References
-
- Tysnes O.B., Storstein A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neural Transmission 124 (2017) 901–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1686-y. 10.1007/s00702-017-1686-y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kouli A., Torsney K.M., Kuan W.-L. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. in: Park. Dis. Pathog. Clin. Asp., 2018: pp. 3–26. https://doi.org/10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch1. 10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ray Dorsey E., Elbaz A., Nichols E., Abd-Allah F., Abdelalim A., et al. . Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Neurology 17 (2018) 939–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30295-3. 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30295-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams U., Bandmann O., Walker R. Parkinson’s Disease in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Review of Epidemiology, Genetics and Access to Care. Journal of Movement Disorders 11 (2018) 53–64. https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.17028. 10.14802/jmd.17028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arisoy S., Sayiner O., Comoglu T., Onal D., Atalay O., Pehlivanoglu B. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of levodopa-loaded nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 25 (2020) 735–747. https://doi.org/10.1080/10837450.2020.1740257. 10.1080/10837450.2020.1740257 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
