Correlation between the Warburg effect and progression of triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 36776368
- PMCID: PMC9913723
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1060495
Correlation between the Warburg effect and progression of triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
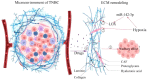
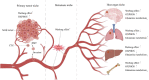
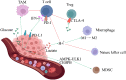
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is ineligible for hormonal therapy and Her-2-targeted therapy due to the negative expression of the estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2. Although targeted therapy and immunotherapy have been shown to attenuate the aggressiveness of TNBC partially, few patients have benefited from them. The conventional treatment for TNBC remains chemotherapy. Chemoresistance, however, impedes therapeutic progress over time, and chemotherapy toxicity increases the burden of cancer on patients. Therefore, introducing more advantageous TNBC treatment options is a necessity. Metabolic reprogramming centered on glucose metabolism is considered a hallmark of tumors. It is described as tumor cells tend to convert glucose to lactate even under normoxic conditions, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect. Similar to Darwinian evolution, its emergence is attributed to the selective pressures formed by the hypoxic microenvironment of pre-malignant lesions. Of note, the Warburg effect does not disappear with changes in the microenvironment after the formation of malignant tumor phenotypes. Instead, it forms a constitutive expression mediated by mutations or epigenetic modifications, providing a robust selective survival advantage for primary and metastatic lesions. Expanding evidence has demonstrated that the Warburg effect mediates multiple invasive behaviors in TNBC, including proliferation, metastasis, recurrence, immune escape, and multidrug resistance. Moreover, the Warburg effect-targeted therapy has been testified to be feasible in inhibiting TNBC progression. However, not all TNBCs are sensitive to glycolysis inhibitors because TNBC cells flexibly switch their metabolic patterns to cope with different survival pressures, namely metabolic plasticity. Between the Warburg effect-targeted medicines and the actual curative effect, metabolic plasticity creates a divide that must be continuously researched and bridged.
Keywords: Warburg effect; basal-like breast cancer; glycolysis; metabolic plasticity; triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Li, Yuan, Song and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lactate Metabolism and Immune Modulation in Breast Cancer: A Focused Review on Triple Negative Breast Tumors.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 26;10:598626. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.598626. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33324565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic phenotypes in triple-negative breast cancer.Tumour Biol. 2013 Jun;34(3):1699-712. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0707-1. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23443971
-
Let-7a-5p inhibits triple-negative breast tumor growth and metastasis through GLUT12-mediated warburg effect.Cancer Lett. 2020 Dec 28;495:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.09.012. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32946964
-
Oligo-Fucoidan supplementation enhances the effect of Olaparib on preventing metastasis and recurrence of triple-negative breast cancer in mice.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Sep 15;29(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00855-6. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36109724 Free PMC article.
-
Progress and pitfalls in the use of immunotherapy for patients with triple negative breast cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022 Jun;31(6):567-591. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2049232. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35240902 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoid receptors orchestrate a convergence of host and cellular stress signals in triple negative breast cancer.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Oct;243:106575. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106575. Epub 2024 Jun 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38950871 Review.
-
Multimodal Phasor Approach to study breast cancer cells invasion in 3D spheroid model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 12:2024.06.10.598307. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.10.598307. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38915530 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Conjugates of 3,5-Bis(arylidene)-4-piperidone and Sesquiterpene Lactones Have an Antitumor Effect via Resetting the Metabolic Phenotype of Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2024 Jun 11;29(12):2765. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122765. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930831 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 expression in breast cancer and its distinct upregulation in triple-negative breast cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;15(7):867-894. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.867. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39071464 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine in breast cancer: targeting the PI3K pathway.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 3;22(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04841-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38172946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

