Role of Nanomedicine-Based Therapeutics in the Treatment of CNS Disorders
- PMID: 36770950
- PMCID: PMC9921752
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031283
Role of Nanomedicine-Based Therapeutics in the Treatment of CNS Disorders
Abstract
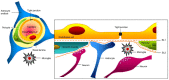
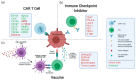
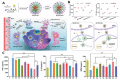
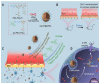
Central nervous system disorders, especially neurodegenerative diseases, are a public health priority and demand a strong scientific response. Various therapy procedures have been used in the past, but their therapeutic value has been insufficient. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier is two of the barriers that protect the central nervous system (CNS), but are the main barriers to medicine delivery into the CNS for treating CNS disorders, such as brain tumors, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Huntington's disease. Nanotechnology-based medicinal approaches deliver valuable cargos targeting molecular and cellular processes with greater safety, efficacy, and specificity than traditional approaches. CNS diseases include a wide range of brain ailments connected to short- and long-term disability. They affect millions of people worldwide and are anticipated to become more common in the coming years. Nanotechnology-based brain therapy could solve the BBB problem. This review analyzes nanomedicine's role in medication delivery; immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and gene therapy are combined with nanomedicines to treat CNS disorders. We also evaluated nanotechnology-based approaches for CNS disease amelioration, with the intention of stimulating the immune system by delivering medications across the BBB.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; central nervous system disorders; immunotherapy; nanomedicine; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Application of Therapeutic Nanoplatforms as a Potential Candidate for the Treatment of CNS Disorders: Challenges and Possibilities.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(33):2742-2757. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220729104433. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35909283 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-based drug delivery for central nervous system disorders.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;143:112117. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112117. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34479020 Review.
-
Nanomedicine-based immunotherapy for central nervous system disorders.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Jul;41(7):936-953. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0429-z. Epub 2020 May 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 32467570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in nanomedicines for diagnosis of central nervous system disorders.Biomaterials. 2021 Feb;269:120492. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120492. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Biomaterials. 2021. PMID: 33153757 Review.
-
Delivering the Promise of Gene Therapy with Nanomedicines in Treating Central Nervous System Diseases.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Sep;9(26):e2201740. doi: 10.1002/advs.202201740. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35851766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
V-ATPase Dysfunction in the Brain: Genetic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities.Cells. 2024 Aug 28;13(17):1441. doi: 10.3390/cells13171441. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in the Application of Nanomedicine in Alzheimer's Disease: A Therapeutic Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 13;24(18):14044. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814044. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)-Crossing Strategies for Improved Treatment of CNS Disorders.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;284:213-230. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_689. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37528323
-
Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Myasthenia Gravis: Advances and Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 11;16(5):651. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050651. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Niosomal Bupropion: Exploring Therapeutic Frontiers through Behavioral Profiling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 12;17(3):366. doi: 10.3390/ph17030366. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tayyba T. Role of extracellular vesicles in human diseases. Biomed. Lett. 2019;5:67–68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

