The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36769643
- PMCID: PMC9918262
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12030995
The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Over the past few years, many studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in treating musculoskeletal conditions. However, there is controversy about its benefits for patients with Achilles tendinopathy.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate whether platelet-rich plasma injections can improve outcomes in patients with Achilles tendinopathy.
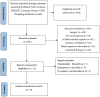
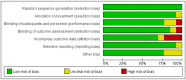
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China Biomedical CD-ROM, and Chinese Science and Technology Journal databases to identify randomised controlled clinical trials that compared the efficacy of PRP injection in patients with Achilles tendinopathy (AT) versus placebo, published between 1 January 1966 and 1 December 2022. Review Manager 5.4.1 software was used for the statistical analysis, and the Jadad score was used to assess the included literature. Only 8 of the 288 articles found met the inclusion criteria.
Results: Our work suggests that: The PRP treatment group had a slightly higher VISA-A score than the placebo group at 6 weeks [MD = 1.92, 95% CI (-0.54, 4.38), I2 = 34%], at 12 weeks [MD = 0.20, 95% CI (-2.65 3.05), I2 = 60%], and 24 weeks [MD = 2.75, 95% CI (-2.76, 8.26), I2 = 87%]). However, the difference was not statistically significant. The Achilles tendon thickness was higher at 12 weeks of treatment in the PRP treatment group compared to the control group [MD = 0.34, 95% CI (-0.04, 0.71), p = 0.08], but the difference was not statistically significant. The VAS-improvement results showed no significant difference at 6 and 24 weeks between the two groups, respectively (MD = 6.75, 95% CI = (-6.12, 19.62), I2 = 69%, p = 0.30), and (MD = 10.46, 95% CI = (-2.44 to 23.37), I2 = 69%, p = 0.11). However, at 12 weeks of treatment, the PRP injection group showed a substantial VAS improvement compared to the control group (MD = 11.30, 95% CI = (7.33 to 15.27), I2 = 0%, p < 0.00001). The difference was statistically significant. The return to exercise rate results showed a higher return to exercise rate in the PRP treatment group than the placebo group [RR = 1.11, 95% CI (0.87, 1.42), p = 0.40]; the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: There is no proof that PRP injections can enhance patient functional and clinical outcomes for Achilles tendinopathy. Augmenting the frequency of PRP injections may boost the outcomes, and additionally, more rigorous designs and standardised clinical randomised controlled trials are needed to produce more reliable and accurate results.
Keywords: Achilles tendinopathy; meta-analysis; platelet-rich plasma; randomised controlled trial; systematic literature review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of Achilles tendon disease.World J Orthop. 2023 Jun 18;14(6):485-501. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i6.485. eCollection 2023 Jun 18. World J Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37377997 Free PMC article.
-
Is Platelet-rich Plasma Injection Effective for Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy? A Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Aug;476(8):1633-1641. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000258. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29601383 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of platelet-rich plasma injection on chronic Achilles tendinopathy and acute Achilles tendon rupture.Platelets. 2022 Apr 3;33(3):339-349. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2021.1961712. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Platelets. 2022. PMID: 34346853 Review.
-
Platelet-rich plasma in chronic Achilles tendinopathy.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023 Dec;33(8):3255-3265. doi: 10.1007/s00590-023-03570-6. Epub 2023 May 24. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023. PMID: 37225947 Review.
-
Platelet-rich plasma injection for the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(16):e15278. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015278. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31008973 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evidence-based orthobiologic practice: Current evidence review and future directions.World J Orthop. 2024 Oct 18;15(10):908-917. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i10.908. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39473516 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Clinical Applications of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Tendinopathy: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2024 Jul 29;16(7):e65636. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65636. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39205774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Medical and Surgical Specialties: Quality, Evaluation, Evidence, and Enforcement.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 5;13(15):4571. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154571. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Informed consent form for platelet rich plasma injections: evidence-based and legally guide for orthopaedic surgeons.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Aug 17;29(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02019-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39152486 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Tendon Injuries in the Servicemember Population across the Spectrum of Pathology: From Exosomes to Bioinductive Scaffolds.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;11(2):158. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020158. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mattila V.M., Huttunen T.T., Haapasalo H., Sillanpää P., Malmivaara A., Pihlajamäki H. Declining incidence of surgery for Achilles tendon rupture follows publication of major RCTs: Evidence-influenced change evident using the Finnish registry study. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2015;49:1084–1086. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092756. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van der Vlist A.C., Winters M., Weir A., Ardern C.L., Welton N.J., Caldwell D.M., Verhaar J.A.N., de Vos R.J. Which treatment is most effective for patients with Achilles tendinopathy? A living systematic review with network meta-analysis of 29 randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2021;55:249–256. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2019-101872. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

