Does the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Bcl-2 Have a Prognostic Significance in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?
- PMID: 36766867
- PMCID: PMC9914895
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11030292
Does the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Bcl-2 Have a Prognostic Significance in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Abstract
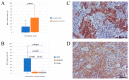
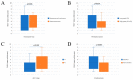
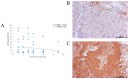
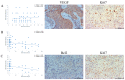
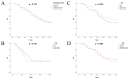
Lung cancer is the most common cause of mortality from malignant tumors worldwide. The five-year survival rate for people with advanced stages varies considerably, from 35.4% to 6.9%. The angiogenic potential of bcl2 is not well known, nor is the way in which tumor cells with excessive bcl2 expression affect VEGF production. Hypothetically, given that tumor growth, progression and metastasis are dependent on angiogenesis, the antiapoptotic effect is expected to form a link between these two molecules. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between bcl-2 and VEGF expression, clinicopathological features and survival in 216 patients with advanced NSCLC. Archival tumor tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry for the expression of bcl-2 and VEGF. Immunoreactivity for bcl-2 was observed in 41.4% of NSCLCs, 51% of squamous and 34.8% of adenocarcinomas-expressed Bcl-2. There was an inverse correlation of mononuclear stromal reaction and bcl-2 expression in adenocarcinoma (p < 0.0005). A total of 71.8% NSCLCs were VEGF positive, 56% of squamous and 82.2% of adenocarcinomas. High level of VEGF expression was significantly associated with histology type (p = 0.043), low histology grade (p = 0.014), clinical stage IV (p = 0.018), smoking history (p = 0.008) and EGFR mutations (p = 0.026). There was an inverse correlation in the expression of Bcl-2 and VEGF in NSCLC patients (p = 0.039, r = -0.163). Two-year survival of patients with unresectable NSCLC was 39.3%, and 50% of patients were alive at 17 months. Our results demonstrated no difference in survival for patients in advanced NSCLC grouped by bcl-2 and VEGF status. Additionally, we observed an inverse correlation in the expression of Bcl-2 and VEGF in NSCLC and mononuclear reaction and bcl-2 expression in adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: VEGF; adenocarcinoma (ACs); bcl-2; non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC); squamous cell carcinoma (SCCs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor, wild-type p53, and angiogenesis in early operable non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Dec;4(12):3017-24. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9865915
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-A and vascular endothelial growth factor-C as prognostic factors for non-small cell lung cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2004 Jun;10(6):BR157-65. Epub 2004 Jun 1. Med Sci Monit. 2004. PMID: 15173661
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor, p53, Rb, Bcl-2 expression and response to chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2004 Oct;46(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.03.018. Lung Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15364135
-
Targeting angiogenesis in squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Drugs. 2014 Mar;74(4):403-13. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0182-z. Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24578213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of anti-apoptosis proteins survivin and bcl-2 in non-small cell lung carcinomas: a clinicopathologic study of 102 cases.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2004 Mar;12(1):44-9. doi: 10.1097/00129039-200403000-00009. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2004. PMID: 15163019 Review.
Cited by
-
Paracrine Regulation and Immune System Pathways in the Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment of Lung Cancer: Insights into Oncogenesis and Immunotherapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 10;16(6):1113. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061113. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Howlader N.N.A., Krapcho M., Miller D., Brest A., Yu M., Ruhl J., Tatalovich Z., Mariotto A., Lewis D.R., Chen H.S., et al., editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2017. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2020. [(accessed on 1 April 2020)]. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/
-
- Gurguş D., Grigoraş M.L., Motoc A.G.M., Zamfir C.L., Cornianu M., Faur C.I., Pop D.L., Folescu R. Clinical relevance and accuracy of p63 and TTF-1 for better approach of small cell lung carcinoma versus poorly differentiated nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol Embryol. 2019;60:139–143. - PubMed
-
- Ma Y., Fan M., Dai L., Kang X., Liu Y., Sun Y., Xiong H., Liang Z., Yan W., Chen K. Expression of p63 and CK5/6 in early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma is not only an early diagnostic indicator but also correlates with a good prognosis. Thorac. Cancer. 2015;6:288–295. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

