Exosomal LncRNAs in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Biological Functions and Emerging Clinical Applications
- PMID: 36765913
- PMCID: PMC9913195
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030959
Exosomal LncRNAs in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Biological Functions and Emerging Clinical Applications
Abstract
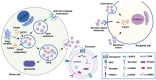
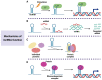
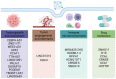
Due to the lack of specific and effective biomarkers and therapeutic targets, the early diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer remain unsatisfactory. As a type of nanosized vesicles derived from living cells, exosomes mediate cell-to-cell communication by transporting bioactive molecules, thus participating in the regulation of many pathophysiological processes. Recent evidence has revealed that several long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are enriched in exosomes. Exosomes-mediated lncRNAs delivery is critically involved in various aspects of gastrointestinal cancer progression, such as tumor proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, stemness, immune microenvironment, and drug resistance. Exosomal lncRNAs represent promising candidates to act as the diagnosis biomarkers and anti-tumor targets. This review introduces the major characteristics of exosomes and lncRNAs and describes the biological functions of exosomal lncRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer development. The preclinical studies on using exosomal lncRNAs to monitor and treat gastrointestinal cancer are also discussed, and the opportunities and challenges for translating them into clinical practice are evaluated.
Keywords: biomarker; exosomes; gastrointestinal cancer; lncRNAs; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biological functions and clinical applications of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(20):11656-11666. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15873. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32924276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal long non-coding RNAs: novel molecules in gastrointestinal cancers' progression and diagnosis.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 14;12:1014949. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1014949. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36591473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer: Interplay, modulation, and therapeutic avenues.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Apr 4;9(3):887-900. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.03.014. eCollection 2024 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38616862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal circRNAs: Novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastrointestinal tumors.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jan;157:114053. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114053. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36462315 Review.
-
Exosomal Long Non-coding RNAs: Emerging Players in the Tumor Microenvironment.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Oct 4;23:1371-1383. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.039. eCollection 2021 Mar 5. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 33738133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the Intricate Roles of Exosomes in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Comprehensive Review of Physiological Significance and Pathological Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15677. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115677. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment Modulation by Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Cells. 2024 Apr 15;13(8):682. doi: 10.3390/cells13080682. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The landscape of lncRNAs in gastric cancer: from molecular mechanisms to potential clinical applications.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 21;14:1237723. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1237723. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37670949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The essential roles of lncRNAs/PI3K/AKT axis in gastrointestinal tumors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 5;12:1442193. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1442193. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39161590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and Transcriptomic Research in the Discovery and Application of Colorectal Cancer Circulating Markers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 3;24(15):12407. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512407. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kashyap S., Pal S., Chandan G., Saini V., Chakrabarti S., Saini N.K., Mittal A., Thakur V.K., Saini A.K., Saini R.V. Understanding the cross-talk between human microbiota and gastrointestinal cancer for developing potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022;86:643–651. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.04.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raza A., Khan A.Q., Inchakalody V.P., Mestiri S., Yoosuf Z., Bedhiafi T., El-Ella D.M.A., Taib N., Hydrose S., Akbar S., et al. Dynamic liquid biopsy components as predictive and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022;41:99. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02318-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- BE2020680/Advanced Science and Technology Foundation of the Jiangsu Province
- 20220516/Technology Development Project of Jiangsu University
- ss2018003/Zhenjiang Key Laboratory of High Technology Research on Exosomes Foundation and Transformation Application
- Phase III/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

