Chemotherapeutic Activity of Pitavastatin in Vincristine Resistant B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 36765664
- PMCID: PMC9913300
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030707
Chemotherapeutic Activity of Pitavastatin in Vincristine Resistant B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
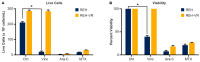
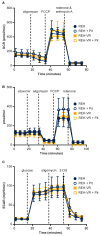
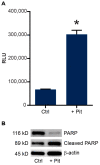
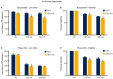
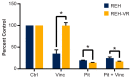
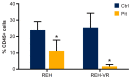
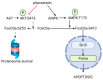
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is derived from an accumulation of malignant, immature B cells in the bone marrow and blood. Relapse due, in part, to the emergence of tumor cells that are resistant to front line standard chemotherapy is associated with poor patient outcomes. This challenge highlights the need for new treatment strategies to eliminate residual chemoresistant tumor cells. Based on the use of pitavastatin in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), we evaluated its efficacy in an REH ALL cell line derived to be resistant to vincristine. We found that pitavastatin inhibited the proliferation of both parental and vincristine-resistant REH tumor cells at an IC50 of 449 nM and 217 nM, respectively. Mitochondrial bioenergetic assays demonstrated that neither vincristine resistance nor pitavastatin treatment affected cellular oxidative phosphorylation, beta-oxidation, or glycolytic metabolism in ALL cells. In a co-culture model of ALL cells with bone marrow stromal cells, pitavastatin significantly decreased cell viability more robustly in the vincristine-resistant ALL cells compared with their parental controls. Subsequently, NSG mice were used to develop an in vivo model of B-cell ALL using both parental and vincristine-resistant ALL cells. Pitavastatin (10 mg/kg i.p.) significantly reduced the number of human CD45+ REH ALL cells in the bone marrow of mice after 4 weeks of treatment. Mechanistic studies showed that pitavastatin treatment in the vincristine-resistant cells led to apoptosis, with increased levels of cleaved PARP and protein-signaling changes for AMP-activated protein kinase/FoxO3a/Puma. Our data suggest the possible repurposing of pitavastatin as a chemotherapeutic agent in a model of vincristine-resistant B-cell ALL.
Keywords: bone marrow; residual disease; sirtuins; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
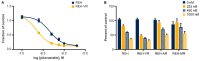

Similar articles
-
Pitavastatin Is Anti-Leukemic in a Bone Marrow Microenvironment Model of B-Lineage Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 28;14(11):2681. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112681. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681662 Free PMC article.
-
The MitoNEET Ligand NL-1 Mediates Antileukemic Activity in Drug-Resistant B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019 Jul;370(1):25-34. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.255984. Epub 2019 Apr 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019. PMID: 31010844 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of miR-155 Promoting Drug Resistance in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by Regulating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Apr;30(2):418-424. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2022.02.016. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35395973 Chinese.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Vincristine Sulfate Liposome Injection in the Treatment of Adult Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia.Oncologist. 2016 Jul;21(7):840-7. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0391. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27328933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anticancer Properties of Pitavastatin against Cervical Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7915. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147915. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moses B.S., Slone W.L., Thomas P., Evans R., Piktel D., Angel P.M., Walsh C.M., Cantrell P.S., Rellick S.L., Martin K.H., et al. Bone marrow microenvironment modulation of acute lymphoblastic leukemia phenotype. Exp. Hematol. 2016;44:50–59. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.09.003. e51-52. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

