The role of Evi/Wntless in exporting Wnt proteins
- PMID: 36763105
- PMCID: PMC10112924
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.201352
The role of Evi/Wntless in exporting Wnt proteins
Abstract
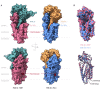
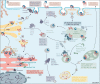
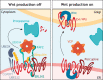
Intercellular communication by Wnt proteins governs many essential processes during development, tissue homeostasis and disease in all metazoans. Many context-dependent effects are initiated in the Wnt-producing cells and depend on the export of lipidated Wnt proteins. Although much focus has been on understanding intracellular Wnt signal transduction, the cellular machinery responsible for Wnt secretion became better understood only recently. After lipid modification by the acyl-transferase Porcupine, Wnt proteins bind their dedicated cargo protein Evi/Wntless for transport and secretion. Evi/Wntless and Porcupine are conserved transmembrane proteins, and their 3D structures were recently determined. In this Review, we summarise studies and structural data highlighting how Wnts are transported from the ER to the plasma membrane, and the role of SNX3-retromer during the recycling of its cargo receptor Evi/Wntless. We also describe the regulation of Wnt export through a post-translational mechanism and review the importance of Wnt secretion for organ development and cancer, and as a future biomarker.
Keywords: Cancer; Development; Evi; PORCN/Porcupine; Wnt secretion; Wnt signalling; Wntless/Wls.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional regulation of Wnt protein through post-translational modifications.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Dec 16;50(6):1797-1808. doi: 10.1042/BST20220735. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 36484635
-
Lipid-independent secretion of a Drosophila Wnt protein.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 20;283(25):17092-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802059200. Epub 2008 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18430724 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective fatty acylation is essential for the release of lipidated WNT proteins from the acyltransferase Porcupine (PORCN).J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 19;294(16):6273-6282. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007268. Epub 2019 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30737280 Free PMC article.
-
Helping Wingless take flight: how WNT proteins are secreted.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;8(4):331-6. doi: 10.1038/nrm2141. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17342185 Review.
-
A dedicated Wnt secretion factor.Cell. 2006 May 5;125(3):432-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.018. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16678089 Review.
Cited by
-
Ehbp1 orchestrates orderly sorting of Wnt/Wingless to the basolateral and apical cell membranes.EMBO Rep. 2024 Nov;25(11):5053-5079. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00289-1. Epub 2024 Oct 14. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39402333 Free PMC article.
-
The origin and evolution of Wnt signalling.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Jul;25(7):500-512. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00699-w. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38374446 Review.
-
Engineered extracellular vesicles enable high-efficient delivery of intracellular therapeutic proteins.Protein Cell. 2024 Oct 1;15(10):724-743. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae015. Protein Cell. 2024. PMID: 38518087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal, P., Zhang, B., Ho, Y., Cook, A., Li, L., Mikhail, F. M., Wang, Y., McLaughlin, M. E. and Bhatia, R. (2017). Enhanced targeting of CML stem and progenitor cells by inhibition of porcupine acyltransferase in combination with TKI. Blood 129, 1008-1020. 10.1182/blood-2016-05-714089 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguilera, K. Y., Le, T., Riahi, R., Lay, A. R., Hinz, S., Saadat, E. A., Vashisht, A. A., Wohlschlegel, J., Donahue, T. R., Radu, C. G.et al. (2022). Porcupine inhibition disrupts mitochondrial function and homeostasis in WNT ligand-addicted pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 21, 936-947. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0623 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

