p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Enhances Reovirus Replication by Facilitating Efficient Virus Entry, Capsid Uncoating, and Postuncoating Steps
- PMID: 36744961
- PMCID: PMC9972948
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00009-23
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Enhances Reovirus Replication by Facilitating Efficient Virus Entry, Capsid Uncoating, and Postuncoating Steps
Abstract
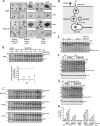
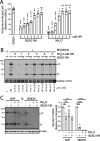
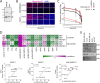
Mammalian orthoreovirus serotype 3 Dearing is an oncolytic virus currently undergoing multiple clinical trials as a potential cancer therapy. Previous clinical trials have emphasized the importance of prescreening patients for prognostic markers to improve therapeutic success. However, only generic cancer markers such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), Hras, Kras, Nras, Braf, and p53 are currently utilized, with limited benefit in predicting therapeutic efficacy. This study aimed to investigate the role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling during reovirus infection. Using a panel of specific p38 MAPK inhibitors and an inactive inhibitor analogue, p38 MAPK signaling was found to be essential for establishment of reovirus infection by enhancing reovirus endocytosis, facilitating efficient reovirus uncoating at the endo-lysosomal stage, and augmenting postuncoating replication steps. Using a broad panel of human breast cancer cell lines, susceptibility to reovirus infection corresponded with virus binding and uncoating efficiency, which strongly correlated with status of the p38β isoform. Together, results suggest p38β isoform as a potential prognostic marker for early stages of reovirus infection that are crucial to successful reovirus infection. IMPORTANCE The use of Pelareorep (mammalian orthoreovirus) as a therapy for metastatic breast cancer has shown promising results in recent clinical trials. However, the selection of prognostic markers to stratify patients has had limited success due to the fact that these markers are upstream receptors and signaling pathways that are present in a high percentage of cancers. This study demonstrates that the mechanism of action of p38 MAPK signaling plays a key role in establishment of reovirus infection at both early entry and late replication steps. Using a panel of breast cancer cell lines, we found that the expression levels of the MAPK11 (p38β) isoform are a strong determinant of reovirus uncoating and infection establishment. Our findings suggest that selecting prognostic markers that target key steps in reovirus replication may improve patient stratification during oncolytic reovirus therapy.
Keywords: breast cancer; oncolytic viruses; p38 MAPK; prognostic indicators; reovirus; virus entry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

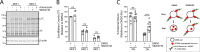

Similar articles
-
Polymorphisms in the Most Oncolytic Reovirus Strain Confer Enhanced Cell Attachment, Transcription, and Single-Step Replication Kinetics.J Virol. 2020 Jan 31;94(4):e01937-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01937-19. Print 2020 Jan 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31776267 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of virion-associated σ1 fibers on oncolytic reovirus variants promotes adaptation toward tumorigenic cells.J Virol. 2015 Apr;89(8):4319-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03651-14. Epub 2015 Feb 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25653434 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Tumor-Associated Metalloproteases Restrict Reovirus Oncolysis by Cleaving the σ1 Cell Attachment Protein and Can Be Overcome by Mutation of σ1.J Virol. 2019 Oct 29;93(22):e01380-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01380-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31462562 Free PMC article.
-
An Orchestra of Reovirus Receptors: Still Searching for the Conductor.Adv Virus Res. 2018;100:223-246. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Adv Virus Res. 2018. PMID: 29551138 Review.
-
Control of Capsid Transformations during Reovirus Entry.Viruses. 2021 Jan 21;13(2):153. doi: 10.3390/v13020153. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33494426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of Reoviral Cytolysis (I): Combination Therapeutics.Viruses. 2023 Jun 29;15(7):1472. doi: 10.3390/v15071472. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernstein V, Ellard SL, Dent SF, Tu D, Mates M, Dhesy-Thind SK, Panasci L, Gelmon KA, Salim M, Song X, Clemons M, Ksienski D, Verma S, Simmons C, Lui H, Chi K, Feilotter H, Hagerman LJ, Seymour L. 2018. A randomized phase II study of weekly paclitaxel with or without pelareorep in patients with metastatic breast cancer: final analysis of Canadian Cancer Trials Group IND.213. Breast Cancer Res Treat 167:485–493. 10.1007/s10549-017-4538-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

