Nutritional aspects and dietary benefits of "Silkworms": Current scenario and future outlook
- PMID: 36742434
- PMCID: PMC9892554
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1121508
Nutritional aspects and dietary benefits of "Silkworms": Current scenario and future outlook
Abstract
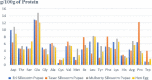
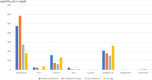
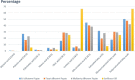
In the current scenario, it is estimated that by 2050, there will be an additional 2.5 billion people and a 70% increase in food demand. Crop yields are not increasing fast enough to support global needs, and world agriculture is facing several serious challenges. Therefore, insects can be a nutritious alternative to meet the ever-increasing food demand in the present and future. The majority of insect consumption occurs in developing countries, with approximately 1,900 insect species consumed worldwide. Food and feed derived from them are of high quality, have a high feed conversion ratio and emit a low level of greenhouse gases. Among insects silkworms are beneficial to humans, not only because of their high nutritional value, but also because of their several pharmacological properties. Silkworm eggs, larvae, and pupae contains high amount of proteins, oils, minerals, vitamins, and several other beneficial components which are nutritious as well as have positive effect on human health. Studies have shown that silkworm pupae protect the liver, enhance immunity, inhibit apoptosis, inhibit cancer, inhibit tumor growth, inhibit microbial growth, regulate blood glucose and blood lipids, and lower blood pressure. This review paper summerized the nutritional value of different life stages of silkworm, nutritional comparison of silkworm with the major human foods, and the effects of silkworm consumption on human health, thus ittargets to generate interest toward in sericulture and improve human health by using silkworm as a nutritious food and attain sustainability in food and nutritional security.
Keywords: consumption; health; insect; nutrition; pupae; silkworm.
Copyright © 2023 Mahanta, Komal, Samal, Bhoi, Dubey, Pradhan, Nekkanti, Gouda, Saini, Negi, Bhateja, Jat and Jeengar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nutritional, functional, and allergenic properties of silkworm pupae.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Jun 29;9(8):4655-4665. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2428. eCollection 2021 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34401111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silkworm Pupae: A Functional Food with Health Benefits for Humans.Foods. 2022 May 28;11(11):1594. doi: 10.3390/foods11111594. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35681343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edible insects in China: Utilization and prospects.Insect Sci. 2018 Apr;25(2):184-198. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12449. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Insect Sci. 2018. PMID: 28225201 Review.
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edible insects are the future?Proc Nutr Soc. 2016 Aug;75(3):294-305. doi: 10.1017/S0029665116000069. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Proc Nutr Soc. 2016. PMID: 26908196
Cited by
-
Insect-pathogen crosstalk and the cellular-molecular mechanisms of insect immunity: uncovering the underlying signaling pathways and immune regulatory function of non-coding RNAs.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1169152. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1169152. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37691928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ad libitum feeding of silkworm larvae powder-containing diets specifically influences metabolism-related and short-chain fatty acid-producing gut bacteria in mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 14;14:1383774. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1383774. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38947126 Free PMC article.
-
An In-Depth Insight into the Profile, Mechanisms, Functions, and Transfer of Essential Amino Acids from Mulberry Leaves to Silkworm Bombyx mori L. Pupae and Fish.Insects. 2024 May 5;15(5):332. doi: 10.3390/insects15050332. Insects. 2024. PMID: 38786888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Genetic Symphony: Harnessing CRISPR-Cas Genome Editing for Effective Insect Pest Management.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;12(23):3961. doi: 10.3390/plants12233961. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating bio-physicochemical properties of raw powder prepared from whole larvae containing liquid silk of the domestic silkworm.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 5;11:1404489. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1404489. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38903626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jongema Y. List of Edible Insects of the World. Wageningen: Laboratory of Entomology, Wageningen University; (2017).
-
- de Castro R, Ohara A, dos Santos Aguilar J, Domingues M. Nutritional, functional and biological properties of insect proteins: processes for obtaining, consumption and future challenges. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2018) 76:82–9. 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.04.006 - DOI
-
- Buhroo Z, Bhat M, Malik M, Kamili A, Ganai N, Khan I. Trends in development and utilization of sericulture resources for diversification and value addition. Int J Entomol Res. (2018) 6:27–47.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

