Inhibition of IL-6 signaling prevents serum-induced umbilical cord artery dysfunction from patients with severe COVID-19
- PMID: 36737252
- PMCID: PMC10026982
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00154.2022
Inhibition of IL-6 signaling prevents serum-induced umbilical cord artery dysfunction from patients with severe COVID-19
Abstract
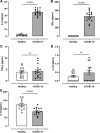
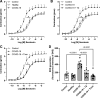
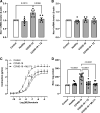
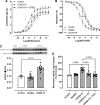
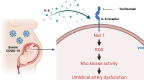
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection has a negative impact on the cytokine profile of pregnant women. Increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines seem to be correlated with the severity of the disease, in addition to predisposing to miscarriage or premature birth. Proinflammatory cytokines increase the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). It is unclear how interleukin-6 (IL-6) found in the circulation of patients with severe COVID-19 might affect gestational health, particularly concerning umbilical cord function. This study tested the hypothesis that IL-6 present in the circulation of women with severe COVID-19 causes umbilical cord artery dysfunction by increasing ROS generation and activating redox-sensitive proteins. Umbilical cord arteries were incubated with serum from healthy women and women with severe COVID-19. Vascular function was assessed using concentration-effect curves to serotonin in the presence or absence of pharmacological agents, such as tocilizumab (antibody against the IL-6 receptor), tiron (ROS scavenger), ML171 (Nox1 inhibitor), and Y27632 (Rho kinase inhibitor). ROS generation was assessed by the dihydroethidine probe and Rho kinase activity by an enzymatic assay. Umbilical arteries exposed to serum from women with severe COVID-19 were hyperreactive to serotonin. This effect was abolished in the presence of tocilizumab, tiron, ML171, and Y27632. In addition, serum from women with severe COVID-19 increased Nox1-dependent ROS generation and Rho kinase activity. Increased Rho kinase activity was abolished by tocilizumab and tiron. Serum cytokines in women with severe COVID-19 promote umbilical artery dysfunction. IL-6 is key to Nox-linked vascular oxidative stress and activation of the Rho kinase pathway.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; Rho kinase; reactive oxygen species; umbilical cord arteries.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Rita Tostes is an editor of
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine storm in individuals with severe COVID-19 decreases endothelial cell antioxidant defense via downregulation of the Nrf2 transcriptional factor.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):H252-H263. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00096.2023. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37327001 Free PMC article.
-
Internal Pudental Artery Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus Is Mediated by NOX1-Derived ROS-, Nrf2-, and Rho Kinase-Dependent Mechanisms.Hypertension. 2016 Oct;68(4):1056-64. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07518. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27528061
-
Reactive oxygen species mediate RhoA/Rho kinase-induced Ca2+ sensitization in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle following chronic hypoxia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):L515-29. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00355.2007. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18621909 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical chorioamnionitis at term V: umbilical cord plasma cytokine profile in the context of a systemic maternal inflammatory response.J Perinat Med. 2016 Jan;44(1):53-76. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2015-0121. J Perinat Med. 2016. PMID: 26360486 Free PMC article.
-
Rho A/Rho kinase: human umbilical artery mRNA expression in normal and pre eclamptic pregnancies and functional role in isoprostane-induced vasoconstriction.Reproduction. 2006 Jul;132(1):169-76. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.01088. Reproduction. 2006. PMID: 16816342
Cited by
-
Cytokine storm in individuals with severe COVID-19 decreases endothelial cell antioxidant defense via downregulation of the Nrf2 transcriptional factor.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):H252-H263. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00096.2023. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37327001 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

