Transcriptomic analysis of asthma and allergic rhinitis reveals CST1 as a biomarker of unified airways
- PMID: 36733482
- PMCID: PMC9888248
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1048195
Transcriptomic analysis of asthma and allergic rhinitis reveals CST1 as a biomarker of unified airways
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is an important risk factor for the development of asthma. The "unified airway" theory considers the upper and lower airways as a morphological and functional whole. However, studies exploring biomarkers linking the upper and lower airways in allergic disease are lacking, which may provide insight into the mechanisms underlying AR comorbid asthma.
Purpose: To integrate bioinformatics techniques to explore biomarkers in airway allergic diseases, and to provide a molecular etiology profile for preventing the development of asthma in AR patients.
Methods: Biomarkers were screened by identifying key genes common between AR and asthma through WGCNA and differential gene analysis. GO and KEGG analyses were performed using DAVID. Immuno-infiltration analysis was performed by CIBERSORTx. The predictive value of CST1 to distinguish Th2-high asthma was determined by ROC curves. GSEA was used to analyze the signaling pathways involved in CST1. TargetScan and miRNet were combined with GSE142237 to construct ceRNA network. CMap was used to explore potential therapeutic drugs.
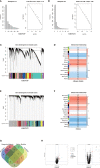
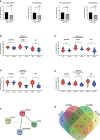
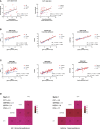
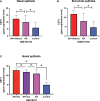
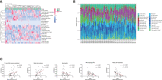
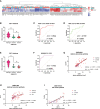
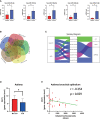
Results: Validation of datasets showed that CST1 was the only gene that was up-regulated in both upper and lower airways in patients with AR and asthma, and correlation heatmaps showed that CST1 was the gene with the highest sum of correlation coefficients. GO and KEGG analysis demonstrated that the lower airways of AR patients were mainly involved in inflammatory and immune responses, similar to asthma. Immune infiltration showed that CST1 was mainly positively correlated with activated CD4 memory T cells. According to the ROC curve, CST1 showed excellent diagnostic efficiency for Th2-high asthma. GSEA indicated that CST1 was involved in the FcϵRI signaling pathway and O-glycan biosynthesis. A ceRNA network including the lncRNAs KCNQ1OT1 and NEAT1 was constructed. Four drugs, including verrucarin-A, had the potential to prevent the development of asthma in AR patients. In addition, corticosteroids were found to downregulate CST1 expression.
Conclusion: CST1 plays a key role in the development of AR comorbid asthma and may be a biomarker for airway allergic diseases. Targeted treatment of CST1 has the potential to prevent the development of asthma in AR patients and deserves further study.
Keywords: CST1; allergic rhinitis; asthma; transcriptomic analysis; unified airways.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Gong, Luo, He, Zhang, Xie, Li and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Susceptibility Genes to Allergic Rhinitis by Gene Expression Data Sets.Clin Transl Sci. 2020 Jan;13(1):169-178. doi: 10.1111/cts.12698. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Clin Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 31794148 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of pathogenic genes and upstream regulators in allergic rhinitis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Dec;115:97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30368403
-
Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Underlying Biomarkers Potentially Linking Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma.Med Sci Monit. 2020 May 27;26:e924934. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924934. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32460303 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic rhinitis and inflammatory airway disease: interactions within the unified airspace.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010 Jul-Aug;24(4):249-54. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2010.24.3499. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010. PMID: 20819460 Review.
-
Comorbidities of asthma and the unified airway.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Sep;5 Suppl 1:S17-22. doi: 10.1002/alr.21615. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 26335831 Review.
Cited by
-
Cysteine protease inhibitor 1 promotes metastasis by mediating an oxidative phosphorylation/MEK/ERK axis in esophageal squamous carcinoma cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;14(1):4985. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55544-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38424293 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation-driven mechanisms of allergic rhinitis during pollen and non-pollen seasons using integrated bioinformatics analysis.Front Genet. 2024 Apr 18;15:1242974. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1242974. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38699230 Free PMC article.
-
Study of molecular patterns associated with ferroptosis in Parkinson's disease and its immune signature.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 21;18(12):e0295699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295699. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38127902 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and analysis for potential clinical diagnostic and prognostic markers in allergic rhinitis.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2670-2682. doi: 10.62347/GKZE5945. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39006280 Free PMC article.
-
The functional role of CST1 and CCL26 in asthma development.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jan;12(1):e1162. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1162. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38270326 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

