Prognostic and diagnostic values of non-coding RNAs as biomarkers for breast cancer: An umbrella review and pan-cancer analysis
- PMID: 36726376
- PMCID: PMC9885171
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1096524
Prognostic and diagnostic values of non-coding RNAs as biomarkers for breast cancer: An umbrella review and pan-cancer analysis
Abstract
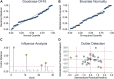
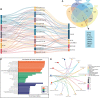
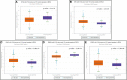
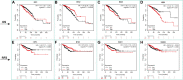
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women. The incidence and morbidity of BC are expected to rise rapidly. The stage at which BC is diagnosed has a significant impact on clinical outcomes. When detected early, an overall 5-year survival rate of up to 90% is possible. Although numerous studies have been conducted to assess the prognostic and diagnostic values of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in breast cancer, their overall potential remains unclear. In this field of study, there are various systematic reviews and meta-analysis studies that report volumes of data. In this study, we tried to collect all these systematic reviews and meta-analysis studies in order to re-analyze their data without any restriction to breast cancer or non-coding RNA type, to make it as comprehensive as possible. Methods: Three databases, namely, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (WoS), were searched to find any relevant meta-analysis studies. After thoroughly searching, the screening of titles, abstracts, and full-text and the quality of all included studies were assessed using the AMSTAR tool. All the required data including hazard ratios (HRs), sensitivity (SENS), and specificity (SPEC) were extracted for further analysis, and all analyses were carried out using Stata. Results: In the prognostic part, our initial search of three databases produced 10,548 articles, of which 58 studies were included in the current study. We assessed the correlation of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) expression with different survival outcomes in breast cancer patients: overall survival (OS) (HR = 1.521), disease-free survival (DFS) (HR = 1.33), recurrence-free survival (RFS) (HR = 1.66), progression-free survival (PFS) (HR = 1.71), metastasis-free survival (MFS) (HR = 0.90), and disease-specific survival (DSS) (HR = 0.37). After eliminating low-quality studies, the results did not change significantly. In the diagnostic part, 22 articles and 30 datasets were retrieved from 8,453 articles. The quality of all studies was determined. The bivariate and random-effects models were used to assess the diagnostic value of ncRNAs. The overall area under the curve (AUC) of ncRNAs in differentiated patients is 0.88 (SENS: 80% and SPEC: 82%). There was no difference in the potential of single and combined ncRNAs in differentiated BC patients. However, the overall potential of microRNAs (miRNAs) is higher than that of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). No evidence of publication bias was found in the current study. Nine miRNAs, four lncRNAs, and five gene targets showed significant OS and RFS between normal and cancer patients based on pan-cancer data analysis, demonstrating their potential prognostic value. Conclusion: The present umbrella review showed that ncRNAs, including lncRNAs and miRNAs, can be used as prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer patients, regardless of the sample sources, ethnicity of patients, and subtype of breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; non-coding RNAs; non-invasive tool; pan-cancer analysis; prognostic and diagnostic.
Copyright © 2023 Bahramy, Zafari, Rajabi, Aghakhani, Jayedi, Khaboushan, Zolbin and Yekaninejad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of non-coding RNAs related to the tumorigenic epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process among ovarian cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e35202. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35202. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39253159 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic value of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2020 Aug;20(3):339-348. doi: 10.1007/s10238-020-00638-z. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32504320 Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic potential of exosome non-coding RNAs in bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 4;14:1336375. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1336375. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38500660 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Non-coding RNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Aug;72(8):1572-1585. doi: 10.1007/s12031-022-01991-2. Epub 2022 Apr 5. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35380333 Review.
Cited by
-
An update on the molecular mechanisms of ZFAS1 as a prognostic, diagnostic, or therapeutic biomarker in cancers.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jun 10;15(1):219. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01078-x. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38856786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA 21 and long non-coding RNAs interplays underlie cancer pathophysiology: A narrative review.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Mar 31;9(3):831-852. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.03.013. eCollection 2024 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38586315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold nanoparticles attenuate the interferon-γ induced SOCS1 expression and activation of NF-κB p65/50 activity via modulation of microRNA-155-5p in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1228458. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1228458. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37720228 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Fabrication of a Nanobiosensor for the Detection of Cell-Free Circulating miRNAS-LncRNAS-mRNAS Triad Grid.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 18;8(43):40677-40684. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05718. eCollection 2023 Oct 31. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37953834 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Circulating miRNAs in the Breast Cancer Neoadjuvant Setting: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;15(13):3424. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133424. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anwar S. L., Sari D. N. I., Kartika A. I., Fitria M. S., Tanjung D. S., Rakhmina D., et al. (2019). Upregulation of circulating MiR-21 expression as a potential biomarker for therapeutic monitoring and clinical outcome in breast cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 20 (4), 1223–1228. 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.4.1223 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

