Vascular Redox Signaling, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling, and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Setting of Transportation Noise Exposure or Chronic Treatment with Organic Nitrates
- PMID: 36719770
- PMCID: PMC10171967
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2023.0006
Vascular Redox Signaling, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling, and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Setting of Transportation Noise Exposure or Chronic Treatment with Organic Nitrates
Abstract
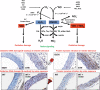
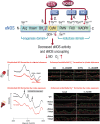
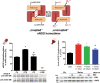
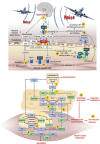
Significance: Cardiovascular disease and drug-induced health side effects are frequently associated with-or even caused by-an imbalance between the concentrations of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) and antioxidants, respectively, determining the metabolism of these harmful oxidants. Recent Advances: According to the "kindling radical" hypothesis, the initial formation of RONS may further trigger the additional activation of RONS formation under certain pathological conditions. The present review specifically focuses on a dysfunctional, uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) caused by RONS in the setting of transportation noise exposure or chronic treatment with organic nitrates, especially nitroglycerin (GTN). We further describe the various "redox switches" that are proposed to be involved in the uncoupling process of eNOS. Critical Issues: In particular, the oxidative depletion of tetrahydrobiopterin and S-glutathionylation of the eNOS reductase domain are highlighted as major pathways for eNOS uncoupling upon noise exposure or GTN treatment. In addition, oxidative disruption of the eNOS dimer, inhibitory phosphorylation of eNOS at the threonine or tyrosine residues, redox-triggered accumulation of asymmetric dimethylarginine, and l-arginine deficiency are discussed as alternative mechanisms of eNOS uncoupling. Future Directions: The clinical consequences of eNOS dysfunction due to uncoupling on cardiovascular disease are summarized also, providing a template for future clinical studies on endothelial dysfunction caused by pharmacological or environmental risk factors.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; nitrate tolerance; nitric oxide synthase uncoupling; oxidative stress; peroxynitrite; superoxide; transportation noise exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
eNOS uncoupling in cardiovascular diseases--the role of oxidative stress and inflammation.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(22):3579-94. doi: 10.2174/13816128113196660748. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24180381 Review.
-
S-glutathionylation reshapes our understanding of endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and nitric oxide/reactive oxygen species-mediated signaling.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 May 15;14(10):1769-75. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.3904. Epub 2011 Mar 27. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21261471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitroglycerin-induced endothelial dysfunction and tolerance involve adverse phosphorylation and S-Glutathionylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase: beneficial effects of therapy with the AT1 receptor blocker telmisartan.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Oct;31(10):2223-31. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.232058. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21757654
-
Electronic cigarette exposure causes vascular endothelial dysfunction due to NADPH oxidase activation and eNOS uncoupling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):H549-H567. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00460.2021. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35089811 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence against tetrahydrobiopterin depletion of vascular tissue exposed to nitric oxide/superoxide or nitroglycerin.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Jan 1;48(1):145-52. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.10.038. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 19853656
Cited by
-
Salidroside enhances NO bioavailability and modulates arginine metabolism to alleviate pulmonary arterial hypertension.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Aug 17;29(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02016-x. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39152472 Free PMC article.
-
Health position paper and redox perspectives - Disease burden by transportation noise.Redox Biol. 2024 Feb;69:102995. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102995. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38142584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming, oxidative stress, and pulmonary hypertension.Redox Biol. 2023 Aug;64:102797. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102797. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37392518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Hypertension: The Insight into Antihypertensive Properties of Vitamins A, C and E.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;13(7):848. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061916 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrams J. The role of nitrates in coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med 1995;155:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Babisch W. Stress hormones in the research on cardiovascular effects of noise. Noise Health 2003;5:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Babisch W. Updated exposure-response relationship between road traffic noise and coronary heart diseases: A meta-analysis. Noise Health 2014;16:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Babisch W, Fromme H, Beyer A, et al. . Increased catecholamine levels in urine in subjects exposed to road traffic noise: The role of stress hormones in noise research. Environ Int 2001;26:475–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

