Differential Plasma Proteins Identified via iTRAQ-Based Analysis Serve as Diagnostic Markers of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36712921
- PMCID: PMC9883097
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5145152
Differential Plasma Proteins Identified via iTRAQ-Based Analysis Serve as Diagnostic Markers of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to identify differentially expressed proteins in the plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer and control subjects, which could serve as potential tumor biomarkers.
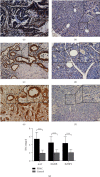
Methods: Differentially expressed proteins were determined via isostatic labeling and absolute quantification (iTRAQ). Potential protein biomarkers were identified via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 40 patients and 40 control subjects, and those eventually selected were further validated in 40 pancreatic cancer and normal pancreatic tissues.
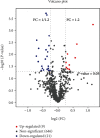
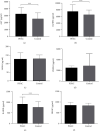
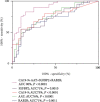
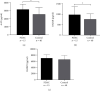
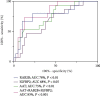
Results: In total, 30 proteins displayed significant differences in expression among which 21 were downregulated and 9 were upregulated compared with the control group. ELISA revealed downregulation of peroxiredoxin-2 (PRDX2) and upregulation of alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), Ras-related protein Rab-2B (RAB2B), insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 (IGFBP2), Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC (RHOC), and prelamin-A/C (LMNA) proteins in 40 other samples of pancreatic cancer. Notably, only AAT, RAB2B, and IGFBP2 levels were consistent with expression patterns obtained with iTRAQ. Moreover, all three proteins displayed a marked increase in pancreatic cancer tissues. Data from ROC curve analysis indicated that the diagnostic ability of AAT, RAB2B, and IGFBP2 combined with carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) for pancreatic cancer was significantly greater than that of the single indexes (area under the curve (AUC): 90% vs. 75% (CA19-9), 76% (AAT), 71% (RAB2B), and 71% (IGFBP2), all P < 0.01).
Conclusion: AAT, RAB2B, and IGFBP2 could serve as effective biomarkers to facilitate the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Xiubing Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of IGFBP2 and IGFBP3 As Compensatory Biomarkers for CA19-9 in Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Using a Combination of Antibody-Based and LC-MS/MS-Based Proteomics.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 31;11(8):e0161009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161009. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27579675 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serum tumor antigen REG4 as a diagnostic biomarker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.J Gastroenterol. 2010;45(1):52-9. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0114-y. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 19789838
-
Periostin and CA242 as potential diagnostic serum biomarkers complementing CA19.9 in detecting pancreatic cancer.Cancer Sci. 2018 Sep;109(9):2841-2851. doi: 10.1111/cas.13712. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29945294 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers in pancreatic cancer: diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive.Cancer J. 2012 Nov-Dec;18(6):530-8. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e31827654ea. Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 23187839 Review.
-
Prognostic and predictive markers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Dig Liver Dis. 2016 Mar;48(3):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Dig Liver Dis. 2016. PMID: 26769569 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics-Driven Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer.Proteomes. 2023 Aug 7;11(3):24. doi: 10.3390/proteomes11030024. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 37606420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

