Genome-wide identification and expression reveal the involvement of the FCS-like zinc finger (FLZ) gene family in Gossypium hirsutum at low temperature
- PMID: 36710860
- PMCID: PMC9879155
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14690
Genome-wide identification and expression reveal the involvement of the FCS-like zinc finger (FLZ) gene family in Gossypium hirsutum at low temperature
Abstract
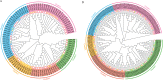
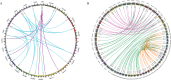
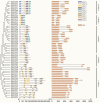
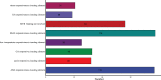
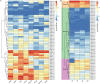
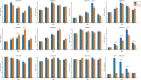
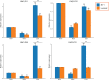
FCS-like zinc finger (FLZ) is a plant-specific gene family that plays an important regulatory role in plant growth and development and its response to stress. However, studies on the characteristics and functions of cotton FLZ family genes are still lacking. This study systematically identified members of the cotton FLZ gene family based on cotton genome data. The cotton FLZ family genes were systematically analyzed by bioinformatics, and their expression patterns in different tissues and under low-temperature stress were analyzed by transcriptome and qRT-PCR. The G. hirsutum genome contains 56 FLZ genes distributed on 20 chromosomes, and most of them are located in the nucleus. According to the number and evolution analysis of FLZ family genes, FLZ family genes can be divided into five subgroups in cotton. The G. hirsutum FLZ gene has a wide range of tissue expression types, among which the expression is generally higher in roots, stems, leaves, receptacles and calyx. Through promoter analysis, it was found that it contained the most cis-acting elements related to methyl jasmonate (MeJA) and abscisic acid (ABA). Combined with the promoter and qRT-PCR results, it was speculated that GhFLZ11, GhFLZ25, GhFLZ44 and GhFLZ55 were involved in the response of cotton to low-temperature stress. Taken together, our findings suggest an important role for the FLZ gene family in the cotton response to cold stress. This study provides an important theoretical basis for further research on the function of the FLZ gene family and the molecular mechanism of the cotton response to low temperature.
Keywords: Cotton; Evolutionary analysis; Expression analysis; FLZ gene family; Low-temperature stress.
© 2023 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Junduo Wang, Yajun Liang, Juyun Zheng, Zhaolong Gong, Xueyuan Li are employees of the Cash Crops Research Institute of Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Science, China. Zhiqiang Li, Guohui Zhou and Yuhui Xu are employed by Adsen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of cotton C2H2-zinc finger transcription factor family and their expression analysis during fiber development.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Sep 11;19(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2003-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31510939 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of ADK Gene Family Members in Cotton under Abiotic Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 17;25(14):7821. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147821. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063069 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of SnRK2 gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).BMC Genet. 2017 Jun 12;18(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12863-017-0517-3. BMC Genet. 2017. PMID: 28606097 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of serine carboxypeptidase-like protein (SCPL) family and functional validation of Gh_SCPL42 unchromosome conferring cotton Verticillium der Verticillium wilt stress in Gossypium hirsutum.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Sep 1;22(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03804-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36045341 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide cloning, identification, classification and functional analysis of cotton heat shock transcription factors in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum).BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 6;15(1):961. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-961. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25378022 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of LPS from Rhodobacter sphaeroides, a Purple Non-Sulfur Bacterium (PNSB), on the Gene Expression of Rice Root.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 28;11(7):1676. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071676. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhtar MN, Farooq A. Environmental impact of bollworms infestation on cotton, Gossypium hirsutum. Pakistan Journal of Zoology. 2019;51(6):2099–2106. doi: 10.17582/journal.pjz/2019.51.6.2099.2106. - DOI
-
- Chang T-H, Wu L-C, Lee T-Y, Chen S-P, Huang H-D, Horng J-T. EuLoc: a web-server for accurately predict protein subcellular localization in eukaryotes by incorporating various features of sequence segments into the general form of Chou’s PseAAC. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 2013;27(1):91–103. doi: 10.1007/s10822-012-9628-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

