Aberrant neurovascular coupling in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: Evidence from a multi-model MRI analysis
- PMID: 36703998
- PMCID: PMC9871937
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1050772
Aberrant neurovascular coupling in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: Evidence from a multi-model MRI analysis
Abstract
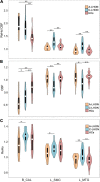
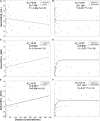
The study aimed to investigate the neurovascular coupling abnormalities in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) and their associations with clinical manifestations. Twenty qualified acute Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (A-LHON, disease duration ≤ 1 year), 29 chronic Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (C-LHON, disease duration > 1 year), as well as 37 healthy controls (HCs) were recruited. The neurovascular coupling strength was quantified as the ratio between regional homogeneity (ReHo), which represents intrinsic neuronal activity and relative cerebral blood flow (CBF), representing microcirculatory blood supply. A one-way analysis of variance was used to compare intergroup differences in ReHo/CBF ratio with gender and age as co-variables. Pearson's Correlation was used to clarify the association between ReHo, CBF, and neurovascular coupling strength. Furthermore, we applied linear and exponential non-linear regression models to explore the associations among ReHo/CBF, disease duration, and neuro-ophthalmological metrics. Compared with HCs, A_LHON, and C_LHON patients demonstrated a higher ReHo/CBF ratio than the HCs in the bilateral primary visual cortex (B_CAL), which was accompanied by reduced CBF while preserved ReHo. Besides, only C_LHON had a higher ReHo/CBF ratio and reduced CBF in the left middle temporal gyrus (L_MTG) and left sensorimotor cortex (L_SMC) than the HCs, which was accompanied by increased ReHo in L_MTG (p < 1.85e-3, Bonferroni correction). A-LHON and C-LHON showed a negative Pearson correlation between ReHo/CBF ratio and CBF in B_CAL, L_SMC, and L_MTG. Only C_LHON showed a weak positive correlation between ReHo/CBF ratio and ReHo in L_SMC and L_MTG (p < 0.05, uncorrected). Finally, disease duration was positively correlated with ReHo/CBF ratio of L_SMC (Exponential: Radj2 = 0.23, p = 8.66e-4, Bonferroni correction). No statistical correlation was found between ReHo/CBF ratio and neuro-ophthalmological metrics (p > 0.05, Bonferroni correction). Brain neurovascular "dyscoupling" within and outside the visual system might be an important neurological mechanism of LHON.
Keywords: Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy; arterial spin labeling; cerebral blood flow; functional magnetic resonance imaging; mitochondrial disease; neurovascular coupling; regional homogeneity.
Copyright © 2023 Ji, Wang, Ding, Tian, Fan, Shi, Yu and Qin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abnormal cerebral blood flow in patients with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.Brain Imaging Behav. 2023 Oct;17(5):471-480. doi: 10.1007/s11682-023-00775-5. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023. PMID: 37368154
-
Abnormal large-scale structural rich club organization in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy.Neuroimage Clin. 2021;30:102619. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102619. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Neuroimage Clin. 2021. PMID: 33752075 Free PMC article.
-
Neurovascular coupling changes in patients with magnetic resonance imaging negative focal epilepsy.Epilepsy Behav. 2023 Jan;138:109035. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.109035. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Epilepsy Behav. 2023. PMID: 36535109
-
[Past, present, and future in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Dec;105(12):809-27. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11802455 Review. Japanese.
-
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: Update on current diagnosis and treatment.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 11;2:1077395. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2022.1077395. eCollection 2022. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38983564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alsop D. C., Detre J. A., Golay X., Gunther M., Hendrikse J., Hernandez-Garcia L., et al. (2015). Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magn. Reson. Med. 73 102–116. 10.1002/mrm.25197 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

