A retrospective clinical study of dolutegravir- versus efavirenz-based regimen in treatment-naïve patients with advanced HIV infection in Nanjing, China
- PMID: 36700216
- PMCID: PMC9868135
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1033098
A retrospective clinical study of dolutegravir- versus efavirenz-based regimen in treatment-naïve patients with advanced HIV infection in Nanjing, China
Abstract
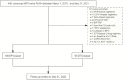
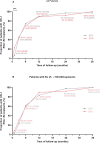
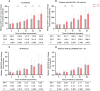
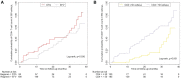
Currently, there are limited data related to the efficacy and safety of ART regimens, as well as factors influencing immune recovery in antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naïve patients with advanced HIV infection, especially in China. We designed a single-center, retrospective cohort study from March 1, 2019, to May 31, 2022, at The Second Hospital of Nanjing, China. ART-naïve adults with advanced HIV infection (CD4+ T-cell count < 200 cells/μL) who met the study criteria were included. The plasma viral load (VL), CD4+ T-cell count, CD4/CD8 ratio, treatment discontinuation, and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) events were collected to compare the efficacy and safety of the dolutegravir (DTG) and the efavirenz (EFV) regimens. Factors of immune recovery were analyzed using the Cox regression model. Study enrolled 285 ART-naïve adults with advanced HIV-1 infection, of which 95 (33.3%) started regimens including DTG and 190 (66.7%) were treated with EFV. After ART initiation, the proportion of patients with HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL was higher (22.5% versus 6.5%, P < 0.001) in those on DTG-based regimens at month 1, but no significant difference at other follow-up points. Compared to the baseline, the median CD4+ T-cell count and CD4/CD8 ratio increased significantly during follow-up both in the EFV and the DTG groups. However, the CD4+ T-cell count increased greater in patients on DTG-based regimens at months 6, 12, 24, and 36 (P < 0.05). A total of 52 (18.2%) patients discontinued treatment, with no significant difference between ART regimens in treatment discontinuation rates. Only 7 patients reported IRIS, without significant difference between ART regimens (P=0.224). Overall, 34.0% (97/285) achieved a CD4+ T-cell count ≥ 350 cells/μL during follow-up. Age (P < 0.001), baseline CD4+ T-cell count (P < 0.001), baseline VL (P < 0.001) and ART regimens (P = 0.019) were associated with the CD4+ T-cell count ≥ 350 cells/μL after adjusting for potential confounders. Among ART-naïve adults with advanced HIV infection, it appeared that DTG-based regimens were better options for initial therapy compared to regimens including EFV; in addition, ART regimens, age, baseline VL and CD4+ T-cell count were associated with immune recovery.
Keywords: IRIS - immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; advanced HIV infection; antiretroviral therapy; dolutegravir; efavirenz; immune recovery.
Copyright © 2023 Zhong, Li, Qi, Su, Yu, Lv, Ye, Zhang, Xu, Cheng, Chen and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunological Efficacy and the Impact on Weight of Dolutegravir-Based Regimen in Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)-Naïve Patients with HIV Infection.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Nov 7;17:4921-4933. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S484703. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39529794 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Safety and Changes in Immunologic and Virologic Parameters of Dolutegravir versus Efavirenz-Based Antiretroviral Therapies Among HIV Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2023 Apr 27;15:173-190. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S396420. eCollection 2023. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 37139483 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Dolutegravir Versus Efavirenz-Based Antiviral Regimen in People Living With HIV-1 in Sichuan Province of China: A Real-World Study.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2022 Oct 1;91(S1):S1-S7. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003041. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2022. PMID: 36094508
-
Dolutegravir Plus Two Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors versus Efavirenz Plus Two Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors As Initial Antiretroviral Therapy for People with HIV: A Systematic Review.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 13;11(10):e0162775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162775. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27736859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrase inhibitors versus efavirenz combination antiretroviral therapies for TB/HIV coinfection: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.AIDS Res Ther. 2021 May 1;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12981-021-00348-w. AIDS Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33933131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events Following Antiretroviral Therapy in People Living with HIV: A Real-World Study of Dynamic Trends and Risk Factors in Hangzhou, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Aug 2;16:5007-5019. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S419308. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37551279 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Efficacy and the Impact on Weight of Dolutegravir-Based Regimen in Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)-Naïve Patients with HIV Infection.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Nov 7;17:4921-4933. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S484703. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39529794 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Safety and Changes in Immunologic and Virologic Parameters of Dolutegravir versus Efavirenz-Based Antiretroviral Therapies Among HIV Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2023 Apr 27;15:173-190. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S396420. eCollection 2023. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 37139483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin K-Y, Cheng C-Y, Li C-W, Yang C-J, Tsai M-S, Liu C-E, et al. . Trends and outcomes of late initiation of combination antiretroviral therapy driven by late presentation among HIV-positive Taiwanese patients in the era of treatment scale-up. PloS One (2017) 12(6):e0179870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179870 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

