The miR-430 locus with extreme promoter density forms a transcription body during the minor wave of zygotic genome activation
- PMID: 36693321
- PMCID: PMC9904021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.12.007
The miR-430 locus with extreme promoter density forms a transcription body during the minor wave of zygotic genome activation
Abstract
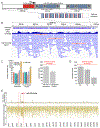
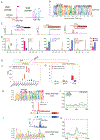
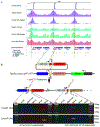
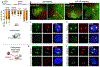
In anamniote embryos, the major wave of zygotic genome activation starts during the mid-blastula transition. However, some genes escape global genome repression, are activated substantially earlier, and contribute to the minor wave of genome activation. The mechanisms underlying the minor wave of genome activation are little understood. We explored the genomic organization and cis-regulatory mechanisms of a transcription body, in which the minor wave of genome activation is first detected in zebrafish. We identified the miR-430 cluster as having excessive copy number and the highest density of Pol-II-transcribed promoters in the genome, and this is required for forming the transcription body. However, this transcription body is not essential for, nor does it encompasse, minor wave transcription globally. Instead, distinct minor-wave-specific promoter architecture suggests that promoter-autonomous mechanisms regulate the minor wave of genome activation. The minor-wave-specific features also suggest distinct transcription initiation mechanisms between the minor and major waves of genome activation.
Keywords: RNA Pol II; core promoter features; miR-430; minor wave; transcription body; zygotic genome activation.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptional Regulation During Zygotic Genome Activation in Zebrafish and Other Anamniote Embryos.Adv Genet. 2016;95:161-94. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Adv Genet. 2016. PMID: 27503357 Review.
-
Two independent transcription initiation codes overlap on vertebrate core promoters.Nature. 2014 Mar 20;507(7492):381-385. doi: 10.1038/nature12974. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24531765 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin facilitates zygotic genome activation in zebrafish.Development. 2018 Jan 3;145(1):dev156521. doi: 10.1242/dev.156521. Development. 2018. PMID: 29158440
-
Protein palmitoylation activate zygotic gene expression during the maternal-to-zygotic transition.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jun 24;475(2):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.074. Epub 2016 May 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27235108
-
Role of MicroRNAs in Zygotic Genome Activation: Modulation of mRNA During Embryogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1605:31-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6988-3_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28456956 Review.
Cited by
-
Rise and SINE: roles of transcription factors and retrotransposons in zygotic genome activation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Jan;26(1):68-79. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00772-6. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39358607
-
Transcription bodies regulate gene expression by sequestering CDK9.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Apr;26(4):604-612. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01389-9. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38589534 Free PMC article.
-
H3K4me2 distinguishes a distinct class of enhancers during the maternal-to-zygotic transition.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 26:2024.08.26.609713. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.26.609713. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253505 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Identifying promoter sequence architectures via a chunking-based algorithm using non-negative matrix factorisation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Nov 20;19(11):e1011491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011491. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37983292 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable elements drive the evolution of metazoan zinc finger genes.Genome Res. 2023 Aug;33(8):1325-1339. doi: 10.1101/gr.277966.123. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Genome Res. 2023. PMID: 37714714 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

