The value of metabolic LncRNAs in predicting prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy of gastric cancer
- PMID: 36686809
- PMCID: PMC9845566
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1019909
The value of metabolic LncRNAs in predicting prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy of gastric cancer
Abstract
Introduction: As a unique feature of malignant tumors, abnormal metabolism can regulate the immune microenvironment of tumors. However, the role of metabolic lncRNAs in predicting the prognosis and immunotherapy of gastric cancer (GC) has not been explored.
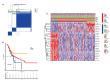
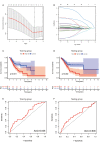
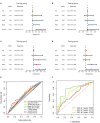
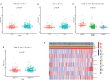
Methods: We downloaded the metabolism-related genes from the GSEA website and identified the metabolic lncRNAs. Co-expression analysis and Lasso Cox regression analysis were utilized to construct the risk model. To value the reliability and sensitivity of the model, Kaplan-Meier analysis and receiver operating characteristic curves were applied. The immune checkpoints, immune cell infiltration and tumor mutation burden of low- and high-risk groups were compared. Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion (TIDE) score was conducted to evaluate the response of GC patients to immunotherapy.
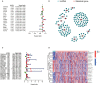
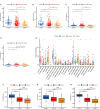
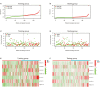
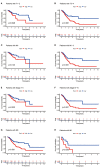
Results: Twenty-three metabolic lncRNAs related to the prognosis of GC were obtained. Three cluster patterns based on metabolic lncRNAs could distinguish GC patients with different overall survival time (OS) effectively (p<0.05). The risk score model established by seven metabolic lncRNAs was verified as an independent prognostic indicator for predicting the OS of GC. The AUC value of the risk model was higher than TNM staging. The high-risk patients were accompanied by significantly increased expression of immune checkpoint molecules (including PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA4) and increased tumor tolerant immune cells, but significantly decreased tumor mutation burden (TMB). Consistently, TIDE values of low-risk patients were significantly lower than that of high-risk patients.
Discussion: The metabolic lncRNAs risk model can reliably and independently predict the prognosis of GC. The feature that simultaneously map the immune status of tumor microenvironment and TMB gives risk model great potential to serve as an indicator of immunotherapy.
Keywords: gastric cancer; immune microenviroment; lncRNA; metabolism; prognosis.
Copyright © 2023 Du, Liu, Patel, Chen, Hu, Huang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis of m6A-related lncRNAs in gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 24;22(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09377-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35331183 Free PMC article.
-
Computational construction of TME-related lncRNAs signature for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Aug;36(8):e24582. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24582. Epub 2022 Jul 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35808868 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-related lncRNA signature predicts prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy in cutaneous melanoma.Front Surg. 2022 Jul 21;9:860806. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.860806. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35937602 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA and its role in gastric cancer immunotherapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 16;11:1052942. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1052942. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36875764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNAs in Immune and Stromal Cells Remodel Phenotype of Cancer Cell and Tumor Microenvironment.J Inflamm Res. 2024 May 17;17:3173-3185. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S460730. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38774447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gastric Cancer Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Applications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241271935. doi: 10.1177/15330338241271935. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39376170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

