Endo-Lysosomal and Autophagy Pathway and Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Mood Disorders: A Review Article
- PMID: 36684613
- PMCID: PMC9849791
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S376380
Endo-Lysosomal and Autophagy Pathway and Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Mood Disorders: A Review Article
Abstract
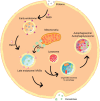
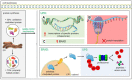
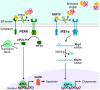
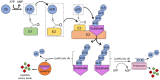
Mood disorders are disabling conditions that cause significant functional impairment. Due to the clinical heterogeneity and complex nature of these disorders, diagnostic and treatment strategies face challenges. The etiology of mood disorders is multifactorial, involving genetic and environmental aspects that are associated with specific biological pathways including inflammation, oxidative stress, and neuroprotection. Alterations in these pathways may reduce the cell's ability to recover from stress conditions occurring during mood episodes. The endo-lysosomal and autophagy pathway (ELAP) and the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) play critical roles in protein homeostasis, impacting neuroplasticity and neurodevelopment. Thus, emerging evidence has suggested a role for these pathways in mental disorders. In the case of neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs), a deeper understanding in the role of ELAP and UPS has been critical to discover new treatment targets. Since it is suggested that NDDs and mood disorders share clinical symptomatology and risk factors, it has been hypothesized that there might be common underlying molecular pathways. Here, we review the importance of the ELAP and UPS for the central nervous system and for mood disorders. Finally, we discuss potential translational strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder associated with these pathways.
Keywords: autophagy; endo-lysosomal pathway; endo-lysosome; mood disorders; neuroplasticity; novel treatments; translational science; treatment target; ubiquitin-proteasome system.
© 2023 Matutino Santos et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A high-throughput screening identifies ZNF418 as a novel regulator of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy-lysosomal pathway.Autophagy. 2021 Oct;17(10):3124-3139. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1856493. Epub 2020 Dec 27. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33249983 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting Nexins in Protein Homeostasis.Cells. 2020 Dec 24;10(1):17. doi: 10.3390/cells10010017. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33374212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in cardiac proteotoxicity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Feb;1852(2):188-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.07.028. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25092168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway by Natural Products: Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Physiol. 2020 Apr 28;11:361. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00361. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32411012 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: CONVERGENCES AND DIVERGENCES IN THE ICD-11 VS. DSM-5 CLASSIFICATION OF MOOD DISORDERS.Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2021;32(4):293-295. doi: 10.5080/u26899. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2021. PMID: 34964106 English, Turkish.
Cited by
-
Dissecting the shared genetic landscape of anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia.J Transl Med. 2024 Apr 18;22(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05153-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38637810 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of autophagy-lysosome dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Nov;25(11):926-946. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00757-5. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39107446 Review.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid exploratory proteomics and ketamine metabolite pharmacokinetics in human volunteers after ketamine infusion.iScience. 2023 Nov 23;26(12):108527. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108527. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38162029 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

