RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36680140
- PMCID: PMC9862891
- DOI: 10.3390/v15010100
RNA Interference Approach Is a Good Strategy against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
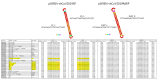
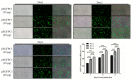
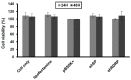
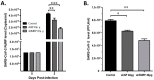
COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, created a devastating outbreak worldwide and consequently became a global health concern. However, no verifiable, specifically targeted treatment has been devised for COVID-19. Several emerging vaccines have been used, but protection has not been satisfactory. The complex genetic composition and high mutation frequency of SARS-CoV-2 have caused an uncertain vaccine response. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based therapy is an efficient strategy to control various infectious diseases employing post-transcriptional gene silencing through the silencing of target complementary mRNA. Here, we designed two highly effective shRNAs targeting the conserved region of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) and spike proteins capable of significant SARS-CoV-2 replication suppression. The efficacy of this approach suggested that the rapid development of an shRNA-based therapeutic strategy might prove to be highly effective in treating COVID-19. However, it needs further clinical trials.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral strategy; shRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Designing an effective therapeutic siRNA to silence RdRp gene of SARS-CoV-2.Infect Genet Evol. 2021 Sep;93:104951. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104951. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Infect Genet Evol. 2021. PMID: 34089909 Free PMC article.
-
A computational approach to design potential siRNA molecules as a prospective tool for silencing nucleocapsid phosphoprotein and surface glycoprotein gene of SARS-CoV-2.Genomics. 2021 Jan;113(1 Pt 1):331-343. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.12.021. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33321203 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 as a therapeutic target.J Med Virol. 2021 Jan;93(1):300-310. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26264. Epub 2020 Jul 19. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32633831 Review.
-
Plant-Derived Natural Non-Nucleoside Analog Inhibitors (NNAIs) against RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Complex (nsp7/nsp8/nsp12) of SARS-CoV-2.J Diet Suppl. 2023;20(2):254-283. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2021.2006387. Epub 2021 Dec 1. J Diet Suppl. 2023. PMID: 34850656
-
Potential of application of the RNA interference phenomenon in the treatment of new coronavirus infection COVID-19.Vopr Virusol. 2021 Sep 16;66(4):241-251. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-61. Vopr Virusol. 2021. PMID: 34545716 Review. English, Russian.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the effect of RNA secondary structure on Cas13d-mediated target RNA cleavage.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jul 20;35(3):102278. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102278. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39220269 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of piRNAs with the mRNA of Candidate Genes in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 23;45(7):6140-6153. doi: 10.3390/cimb45070387. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504303 Free PMC article.
-
Polypurine reverse hoogsteen hairpins as a therapeutic tool for SARS-CoV-2 infection.J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107884. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107884. Epub 2024 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39395809 Free PMC article.
-
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based therapeutic applications against viruses: principles, potential, and challenges.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Oct 16;30(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00981-9. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37845731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Y., Almazi J.G., Ong H.X., Johansen M.D., Ledger S., Traini D., Hansbro P.M., Kelleher A.D., Ahlenstiel C.L. Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms for RNAi Therapeutics Targeting COVID-19 Disease in the Respiratory Tract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:2408. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052408. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fernandes Q., Inchakalody V.P., Merhi M., Mestiri S., Taib N., Moustafa Abo El-Ella D., Bedhiafi T., Raza A., Al-Zaidan L., Mohsen M.O., et al. Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines. Ann. Med. 2022;54:524–540. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2031274. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

