High-Level rAAV Vector Production by rAdV-Mediated Amplification of Small Amounts of Input Vector
- PMID: 36680104
- PMCID: PMC9867474
- DOI: 10.3390/v15010064
High-Level rAAV Vector Production by rAdV-Mediated Amplification of Small Amounts of Input Vector
Abstract
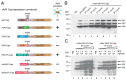
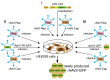
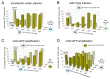
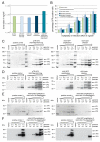
The successful application of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors for long-term transgene expression in clinical studies requires scalable production methods with genetically stable components. Due to their simple production scheme and the high viral titers achievable, first generation recombinant adenoviruses (rAdV) have long been taken into consideration as suitable tools for simultaneously providing both the helper functions and the AAV rep and cap genes for rAAV packaging. So far, however, such rAdV-rep/cap vectors have been difficult to generate and often turned out to be genetically unstable. Through ablation of cis and trans inhibitory function in the AAV-2 genome we have succeeded in establishing separate and stable rAdVs for high-level AAV serotype 2 Rep and Cap expression. These allowed rAAV-2 production at high burst sizes by simple coinfection protocols after providing the AAV-ITR flanked transgene vector genome either as rAAV-2 particles at low input concentrations or in form of an additional rAdV. With characteristics such as the ease of producing the required components, the straightforward adaption to other transgenes and the possible extension to further serotypes or capsid variants, especially the rAdV-mediated rAAV amplification system presents a very promising candidate for up-scaling to clinical grade vector preparations.
Keywords: RIS-Ad; adeno-associated virus; rAAV packaging; recombinant adenovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
S.W. is an inventor on European and International patent applications addressing the rAdV-mediated rAAV vector packaging technology described in this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2 replication and packaging is entirely supported by a herpes simplex virus type 1 amplicon expressing Rep and Cap.J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8780-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.11.8780-8789.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9343238 Free PMC article.
-
AAV production in stable packaging cells requires expression of adenovirus 22/33K protein to allow episomal amplification of integrated rep/cap genes.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 7;13(1):21670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48901-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38066084 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of rep-cap genes is essential for the high-efficiency production of recombinant AAV.Hum Gene Ther. 1997 Jan 1;8(1):87-98. doi: 10.1089/hum.1997.8.1-87. Hum Gene Ther. 1997. PMID: 8989998
-
Expressing Transgenes That Exceed the Packaging Capacity of Adeno-Associated Virus Capsids.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2016 Feb;27(1):1-12. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2015.140. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2016. PMID: 26757051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular design for recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vector production.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Feb;102(3):1045-1054. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8670-1. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29204900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
rAAV Manufacturing: The Challenges of Soft Sensing during Upstream Processing.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Feb 8;10(2):229. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020229. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Pass Tangential Flow Filtration (SPTFF) of Nanoparticles: Achieving Sustainable Operation with Dilute Colloidal Suspensions for Gene Therapy Applications.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 15;13(4):433. doi: 10.3390/membranes13040433. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37103860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaudet D., Méthot J., Déry S., Brisson D., Essiembre C., Tremblay G., Tremblay K., de Wal J., Twisk J., van den Bulk N., et al. Efficacy and long-term safety of alipogene tiparvovec (AAV1-LPLS447X) gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase deficiency: An open-label trial. Gene Ther. 2012;20:361–369. doi: 10.1038/gt.2012.43. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- A Maguire A.M., High K.A., Auricchio A., Wright J.F., Pierce E.A., Testa F., Mingozzi F., Bennicelli J.L., Ying G.-S., Rossi S., et al. Age-dependent effects of RPE65 gene therapy for Leber’s congenital amaurosis: A phase 1 dose-escalation t trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1597–1605. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61836-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Testa F., Maguire A.M., Rossi S., Pierce E.A., Melillo P., Marshall K., Banfi S., Surace E.M., Sun J., Acerra C., et al. Three-year follow-up after unilateral subretinal delivery of adeno-associated virus in patients with Leber congenital Amaurosis type 2. Ophthalmology. 2013;120:1283–1291. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.11.048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

