The Implication of Topoisomerase II Inhibitors in Synthetic Lethality for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 36678591
- PMCID: PMC9866718
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16010094
The Implication of Topoisomerase II Inhibitors in Synthetic Lethality for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
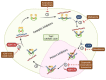
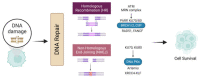
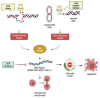
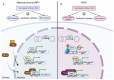
DNA topoisomerase II (Top2) is essential for all eukaryotic cells in the regulation of DNA topology through the generation of temporary double-strand breaks. Cancer cells acquire enhanced Top2 functions to cope with the stress generated by transcription and DNA replication during rapid cell division since cancer driver genes such as Myc and EZH2 hijack Top2 in order to realize their oncogenic transcriptomes for cell growth and tumor progression. Inhibitors of Top2 are therefore designed to target Top2 to trap it on DNA, subsequently causing protein-linked DNA breaks, a halt to the cell cycle, and ultimately cell death. Despite the effectiveness of these inhibitors, cancer cells can develop resistance to them, thereby limiting their therapeutic utility. To maximize the therapeutic potential of Top2 inhibitors, combination therapies to co-target Top2 with DNA damage repair (DDR) machinery and oncogenic pathways have been proposed to induce synthetic lethality for more thorough tumor suppression. In this review, we will discuss the mode of action of Top2 inhibitors and their potential applications in cancer treatments.
Keywords: DNA damage repair; DNA repair inhibitors; DNA topoisomerase II; EZH2; Myc; synthetic lethality; topoisomerase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppressing proteasome mediated processing of topoisomerase II DNA-protein complexes preserves genome integrity.Elife. 2020 Feb 14;9:e53447. doi: 10.7554/eLife.53447. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32057297 Free PMC article.
-
Differential and common DNA repair pathways for topoisomerase I- and II-targeted drugs in a genetic DT40 repair cell screen panel.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Jan;13(1):214-20. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0551. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24130054 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms to Repair Stalled Topoisomerase II-DNA Covalent Complexes.Mol Pharmacol. 2022 Jan;101(1):24-32. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000374. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34689119 Review.
-
Functions of the CSB Protein at Topoisomerase 2 Inhibitors-Induced DNA Lesions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 22;9:727836. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.727836. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34746125 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of topoisomerase II stability and activity by ubiquitination and SUMOylation: clinical implications for cancer chemotherapy.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Sep;48(9):6589-6601. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06665-7. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34476738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9 system: a novel approach to overcome chemotherapy and radiotherapy resistance in cancer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 19. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03480-2. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39560750 Review.
-
New multifunctional hybrids as modulators of apoptosis markers and topoisomerase II in breast cancer therapy: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in silico studies.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 6;14(39):28555-28568. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04219k. eCollection 2024 Sep 4. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39247509 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antiproliferative evaluation of novel 3,5,8-trisubstituted coumarins against breast cancer.Future Med Chem. 2024;16(11):1053-1073. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2023-0375. Epub 2024 May 6. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38708686
-
Network-based identification of key proteins and repositioning of drugs for non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Apr;7(4):e2031. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2031. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38600056 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in Combination Chemotherapy for Colorectal and Breast Cancers with Topoisomerase Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 8;24(9):8457. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098457. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

