Identification of Side Chain Oxidized Sterols as Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists with Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 36674804
- PMCID: PMC9863018
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24021290
Identification of Side Chain Oxidized Sterols as Novel Liver X Receptor Agonists with Therapeutic Potential in the Treatment of Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
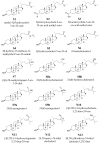
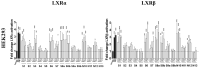
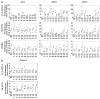
The nuclear receptors-liver X receptors (LXR α and β) are potential therapeutic targets in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases because of their key role in the regulation of lipid homeostasis and inflammatory processes. Specific oxy(phyto)sterols differentially modulate the transcriptional activity of LXRs providing opportunities to develop compounds with improved therapeutic characteristics. We isolated oxyphytosterols from Sargassum fusiforme and synthesized sidechain oxidized sterol derivatives. Five 24-oxidized sterols demonstrated a high potency for LXRα/β activation in luciferase reporter assays and induction of LXR-target genes APOE, ABCA1 and ABCG1 involved in cellular cholesterol turnover in cultured cells: methyl 3β-hydroxychol-5-en-24-oate (S1), methyl (3β)-3-aldehydeoxychol-5-en-24-oate (S2), 24-ketocholesterol (S6), (3β,22E)-3-hydroxycholesta-5,22-dien-24-one (N10) and fucosterol-24,28 epoxide (N12). These compounds induced SREBF1 but not SREBP1c-mediated lipogenic genes such as SCD1, ACACA and FASN in HepG2 cells or astrocytoma cells. Moreover, S2 and S6 enhanced cholesterol efflux from HepG2 cells. All five oxysterols induced production of the endogenous LXR agonists 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol by upregulating the CYP46A1, encoding the enzyme converting cholesterol into 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol; S1 and S6 may also act via the upregulation of desmosterol production. Thus, we identified five novel LXR-activating 24-oxidized sterols with a potential for therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; LXR agonists; cardiovascular disease; cholesterol efflux; oxidized sterols.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest that might be perceived as influencing the impartiality of the reported research.
Figures

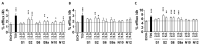


Similar articles
-
Activation of Liver X Receptors and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors by Lipid Extracts of Brown Seaweeds: A Potential Application in Alzheimer's Disease?Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):3004. doi: 10.3390/nu15133004. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447330 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol intermediates from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway as liver X receptor ligands.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 22;281(38):27816-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603781200. Epub 2006 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16857673
-
Induction of intestinal ATP-binding cassette transporters by a phytosterol-derived liver X receptor agonist.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):36091-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304153200. Epub 2003 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12847102
-
Liver X receptors (LXRs). Part I: structure, function, regulation of activity, and role in lipid metabolism.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2007 Dec 3;61:736-59. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2007. PMID: 18063918 Review.
-
LXR agonists: new potential therapeutic drug for neurodegenerative diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;48(3):715-28. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8461-3. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23625315 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Applications of Oxysterols and Derivatives in Age-Related Diseases, Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases, and Cancers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1440:379-400. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-43883-7_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38036890 Review.
-
Flindissone, a Limonoid Isolated from Trichilia prieuriana, Is an LXR Agonist.J Nat Prod. 2023 Aug 25;86(8):1901-1909. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00059. Epub 2023 Aug 1. J Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 37526502 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic Exercise Facilitates the Nuclear Translocation of SREBP2 by Activating AKT/SEC24D to Contribute Cholesterol Homeostasis for Improving Cognition in APP/PS1 Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 16;24(16):12847. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612847. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629027 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of the Cholesterol Transfer Inhibitor U18666A as a Potent Research Tool for the Study of Cholesterol Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;61(6):3503-3527. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03798-7. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37995080 Review.
-
Activation of Liver X Receptors and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors by Lipid Extracts of Brown Seaweeds: A Potential Application in Alzheimer's Disease?Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):3004. doi: 10.3390/nu15133004. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramírez C.M., Torrecilla-Parra M., Pardo-Marqués V., de-Frutos M.F., Pérez-García A., Tabraue C., de la Rosa J.V., Martín-Rodriguez P., Díaz-Sarmiento M., Nuñez U., et al. Crosstalk Between LXR and Caveolin-1 Signaling Supports Cholesterol Efflux and Anti-Inflammatory Pathways in Macrophages. Front. Endocrinol. 2021;12:635923. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635923. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

