Engineering Advanced Drug Delivery Systems for Dry Eye: A Review
- PMID: 36671625
- PMCID: PMC9854618
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10010053
Engineering Advanced Drug Delivery Systems for Dry Eye: A Review
Abstract
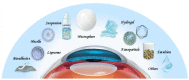
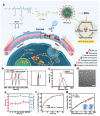
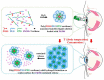
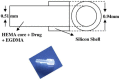
Dry eye disease (DED) is a widespread and frequently reported multifactorial ocular disease that not only causes ocular discomfort but also damages the cornea and conjunctiva. At present, topical administration is the most common treatment modality for DED. Due to the existence of multiple biological barriers, instilled drugs generally exhibit short action times and poor penetration on the ocular surface. To resolve these issues, several advanced drug delivery systems have been proposed. This review discusses new dosage forms of drugs for the treatment of DED in terms of their characteristics and advantages. Innovative formulations that are currently available in the market and under clinical investigation are elaborated. Meanwhile, their deficiencies are discussed. It is envisioned that the flourishing of advanced drug delivery systems will lead to improved management of DED in the near future.
Keywords: drug delivery; dry eye disease; new dosage forms; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Formulation Considerations for the Management of Dry Eye Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Feb 3;13(2):207. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020207. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33546193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Nano-ophthalmology in Treating Dry Eye Disease.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020;8(4):258-289. doi: 10.2174/2211738508666200628034227. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32600244 Review.
-
Current trends in pharmaceutical treatment of dry eye disease: A review.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Aug 1;175:106206. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106206. Epub 2022 May 11. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35568107 Review.
-
Dry eye disease treatment: the role of tear substitutes, their future, and an updated classification.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Sep;24(17):8642-8652. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202009_22801. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32964952 Review.
-
In situ metabolic profile and spatial distribution of ocular tissues: New insights into dry eye disease.Ocul Surf. 2022 Apr;24:51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2021.12.013. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Ocul Surf. 2022. PMID: 34990847
Cited by
-
Recent progress of nanomedicine in managing dry eye disease.Adv Ophthalmol Pract Res. 2024 Jan 29;4(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.aopr.2024.01.008. eCollection 2024 Feb-Mar. Adv Ophthalmol Pract Res. 2024. PMID: 38356795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodegradable Polymer-Based Drug-Delivery Systems for Ocular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 19;24(16):12976. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612976. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on Biodegradable Formulations for Ocular Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 22;15(3):734. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030734. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

