Type 2 diabetes candidate genes, including PAX5, cause impaired insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets
- PMID: 36656641
- PMCID: PMC9927941
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI163612
Type 2 diabetes candidate genes, including PAX5, cause impaired insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets
Abstract
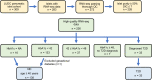
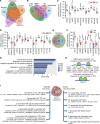
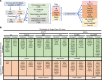
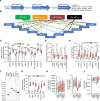
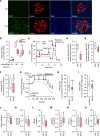
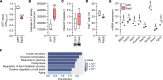
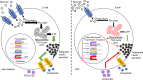
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is caused by insufficient insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells. To identify candidate genes contributing to T2D pathophysiology, we studied human pancreatic islets from approximately 300 individuals. We found 395 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in islets from individuals with T2D, including, to our knowledge, novel (OPRD1, PAX5, TET1) and previously identified (CHL1, GLRA1, IAPP) candidates. A third of the identified expression changes in islets may predispose to diabetes, as expression of these genes associated with HbA1c in individuals not previously diagnosed with T2D. Most DEGs were expressed in human β cells, based on single-cell RNA-Seq data. Additionally, DEGs displayed alterations in open chromatin and associated with T2D SNPs. Mouse KO strains demonstrated that the identified T2D-associated candidate genes regulate glucose homeostasis and body composition in vivo. Functional validation showed that mimicking T2D-associated changes for OPRD1, PAX5, and SLC2A2 impaired insulin secretion. Impairments in Pax5-overexpressing β cells were due to severe mitochondrial dysfunction. Finally, we discovered PAX5 as a potential transcriptional regulator of many T2D-associated DEGs in human islets. Overall, we have identified molecular alterations in human pancreatic islets that contribute to β cell dysfunction in T2D pathophysiology.
Keywords: Beta cells; Diabetes; Endocrinology; Insulin; Metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of human pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic donors identifies candidate genes that influence insulin secretion.PLoS Genet. 2014 Mar 6;10(3):e1004160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004160. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24603685 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing of Human Pancreatic Islets Reveals Novel Differentially Methylated Regions in Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis.Diabetes. 2017 Apr;66(4):1074-1085. doi: 10.2337/db16-0996. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28052964
-
Genes with epigenetic alterations in human pancreatic islets impact mitochondrial function, insulin secretion, and type 2 diabetes.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 12;14(1):8040. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43719-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38086799 Free PMC article.
-
Does epigenetic dysregulation of pancreatic islets contribute to impaired insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes?Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;93(5):511-21. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2015-0057. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26369706 Review.
-
Transcribing β-cell mitochondria in health and disease.Mol Metab. 2017 May 31;6(9):1040-1051. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.05.014. eCollection 2017 Sep. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28951827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TET (Ten-eleven translocation) family proteins: structure, biological functions and applications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Aug 11;8(1):297. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01537-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37563110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics analysis to reveal the potential comorbidity mechanism in psoriasis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Skin Res Technol. 2023 Sep;29(9):e13457. doi: 10.1111/srt.13457. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37753698 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer analysis of SLC2A family genes as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 13;10(8):e29655. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29655. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38655365 Free PMC article.
-
IGFBP7 is upregulated in islets from T2D donors and reduces insulin secretion.iScience. 2024 Aug 20;27(9):110767. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110767. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39280605 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq transcriptome profiling of Nile rat livers reveals novel insights on the anti-diabetic mechanisms of Water-Soluble Palm Fruit Extract.J Appl Genet. 2024 Dec;65(4):867-895. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00880-1. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38890243
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

