Multi-scale Multi-structure Siamese Network (MMSNet) for Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Prediction
- PMID: 36656619
- PMCID: PMC9844668
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-21014-3_45
Multi-scale Multi-structure Siamese Network (MMSNet) for Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Prediction
Abstract
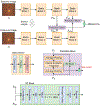
Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness in the United States and worldwide. POAG prediction before onset plays an important role in early treatment. Although deep learning methods have been proposed to predict POAG, these methods mainly focus on current status prediction. In addition, all these methods used a single image as input. On the other hand, glaucoma specialists determine a glaucomatous eye by comparing the follow-up optic nerve image with the baseline along with supplementary clinical data. To simulate this process, we proposed a Multi-scale Multi-structure Siamese Network (MMSNet) to predict future POAG event from fundus photographs. The MMSNet consists of two side-outputs for deep supervision and 2D blocks to utilize two-dimensional features to assist classification. The MMSNet network was trained and evaluated on a large dataset: 37,339 fundus photographs from 1,636 Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS) participants. Extensive experiments show that MMSNet outperforms the state-of-the-art on two "POAG prediction before onset" tasks. Our AUC are 0.9312 and 0.9507, which are 0.2204 and 0.1490 higher than the state-of-the-art, respectively. In addition, an ablation study is performed to check the contribution of different components. These results highlight the potential of deep learning to assist and enhance the prediction of future POAG event. The proposed network will be publicly available on https://github.com/bionlplab/MMSNet.
Keywords: Deep learning; Fundus photographs; Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG); Siamese network.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Diagnosis from Optic Disc Photographs Using a Siamese Network.Ophthalmol Sci. 2022 Aug 13;2(4):100209. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2022.100209. eCollection 2022 Dec. Ophthalmol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36531584 Free PMC article.
-
Automated diagnosing primary open-angle glaucoma from fundus image by simulating human's grading with deep learning.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 18;12(1):14080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17753-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35982106 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting Glaucoma in the Ocular Hypertension Study Using Deep Learning.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr 1;140(4):383-391. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.0244. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35297959 Free PMC article.
-
[A challenge to primary open-angle glaucoma including normal-pressure. Clinical problems and their scientific solution].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012 Mar;116(3):233-67; discussion 268. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22568103 Review. Japanese.
-
Biomarkers and special features of oxidative stress in the anterior segment of the eye linked to lens cataract and the trabecular meshwork injury in primary open-angle glaucoma: challenges of dual combination therapy with N-acetylcarnosine lubricant eye drops and oral formulation of nonhydrolyzed carnosine.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;26(1):86-117. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2011.00969.x. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21883446 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the power of longitudinal medical imaging for eye disease prognosis using Transformer-based sequence modeling.NPJ Digit Med. 2024 Aug 16;7(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41746-024-01207-4. NPJ Digit Med. 2024. PMID: 39152209 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the power of longitudinal medical imaging for eye disease prognosis using Transformer-based sequence modeling.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 30:arXiv:2405.08780v2. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: NPJ Digit Med. 2024 Aug 16;7(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41746-024-01207-4. PMID: 39371086 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bourne RR, et al.: Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 1(6), e339–e349 (2013) - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Xu Y, Wong DWK, Wong TY, Liu J: Glaucoma detection based on deep convolutional neural network. In: 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 715–718. IEEE; (2015) - PubMed
-
- Doshi V, Ying-Lai M, Azen SP, Varma R, Los Angeles Latino Eye Study Group, et al.: Sociodemographic, family history, and lifestyle risk factors for open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension: the Los Angeles Latino Eye Study. Ophthalmology 115(4), 639–647 (2008) - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources