Evaluation of Caralluma edulis for its Potential Against Obesity, Atherosclerosis and Hypertension
- PMID: 36655145
- PMCID: PMC9841870
- DOI: 10.1177/15593258231152112
Evaluation of Caralluma edulis for its Potential Against Obesity, Atherosclerosis and Hypertension
Abstract
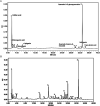
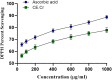
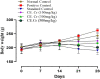
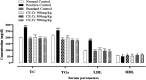
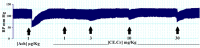
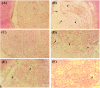
Obesity, a chronic metabolic condition, is an increase in fat mass and blood lipid levels mainly causing atherosclerosis and hypertension, which further lead to cardiovascular complications. The objective of the study was to investigate the crude extract of Caralluma edulis (CE.Cr) for its potential against high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity and its related complications. Hyperlipidemia was induced in Wistar albino rats with HFD (1% cholesterol + 0.5% cholic acid) for 28 days. Treatment groups were administered with different doses of CE.Cr (100, 300 and 500 mg/Kg, p.o.) and the standard group received atorvastatin. At the end of study, sera were analyzed for biochemical markers and the aorta was dissected for microscopic examination. Antioxidant potential was evaluated and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis was performed. The hypotensive potential of CE.Cr was evaluated through an invasive technique. HPLC analysis of CE.Cr showed the presence of chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, apigenin and naringenin. Histological examination of the aorta section showed anti-atherosclerotic effects which were also evident from decrease in serum total cholesterol, triglycerides and low-density lipoproteins levels. CE.Cr decreased mean arterial blood pressure and evoked significant hypotensive effects. The crude extract of C. edulis showed anti-obesity, antihypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic and antioxidant potential.
Keywords: Caralluma edulis; atherosclerosis; high-fat diet; hyperlipidemia; hypertension; obesity.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential Lipid-Lowering Effects of Eleusine indica (L) Gaertn. Extract on High-Fat-Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jan;13(Suppl 1):S1-S9. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.203986. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28479718 Free PMC article.
-
Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) extract treatment improves triglyceridemia, liver cholesterol, liver steatosis, oxidative damage and corticosteronemia in rats rendered obese by high fat diet.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Aug;57(5):1829-1844. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1467-2. Epub 2017 May 13. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28501921
-
Anti-atherosclerosis of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from Rhodiola rosea on rat model via hypolipemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities together with regulation of endothelial function.Phytomedicine. 2018 Dec 1;51:171-180. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466614
-
Effect of Carnitine and herbal mixture extract on obesity induced by high fat diet in rats.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2009 Oct 16;1(1):17. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-1-17. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2009. PMID: 19835614 Free PMC article.
-
Caralluma edulis (Apocynaceae): A Comprehensive Review on its Traditional Uses, Phytochemical Profile and Pharmacological Effects.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(18):1501-1514. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220527092825. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35638276 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Advance of Chinese Medicine in Treating Atherosclerosis: Focus on Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Mar;30(3):277-288. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3611-6. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38057549 Review.
References
-
- Choi H, Eo H, Park K, et al. A water-soluble extract from Cucurbita moschata shows anti-obesity effects by controlling lipid metabolism in a high fat diet-induced obesity mouse model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359(3):419-425. - PubMed
-
- Kolodgie FD, Narula J, Guillo P, Virmani R. Apoptosis in human atherosclerotic plaques. Apoptosis. 1999;4(1):5-10. - PubMed
-
- Xiong C, Peng Y, Liu B, Cui W, Liu X. Anti-obesity, anti-atherosclerotic and anti-oxidant effects of Pu-Erh tea on a high fat diet-induced obese rat model. J Biosci Med. 2019;7(02):120-130.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

